# 起步
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/babel-standalone@6/babel.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
const VDOM = (<h1>Hello, world!</h1>);
ReactDOM.render(VDOM,document.getElementById('app'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- vue中的
h函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/babel-standalone@6/babel.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
const VDOM = React.createElement('h1', {id: 'haha'}, '你好,react');
ReactDOM.render(VDOM,document.getElementById('app'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
npx create-react-app my-app
1
- 用到知识点:
- 类组件
- props传参
- 组件状态管理
- 无状态函数式组件
- 数组状态更改用concat/slice生成新数组再操作,避免使用同一引用的对象/数组
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
// 无状态函数式组件
function Square(props) {
return (
<button className="square" onClick={() => props.onClick()}>
{ props.value }
</button>
);
}
class Board extends React.Component {
// 子组件调用、传参
renderSquare(i) {
return <Square value={this.props.squares[i]} onClick={() => this.props.handleClick(i)}/>;
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(0)}
{this.renderSquare(1)}
{this.renderSquare(2)}
</div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(3)}
{this.renderSquare(4)}
{this.renderSquare(5)}
</div>
<div className="board-row">
{this.renderSquare(6)}
{this.renderSquare(7)}
{this.renderSquare(8)}
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
class Game extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
// 初始化固定长度数组写法
history: [ Array(9).fill(null) ],
xIsNext: true,
}
}
calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
// 成功返回成功的棋子型号,无则返回null
const successIdx = lines.findIndex(([a, b, c]) => squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]);
if (successIdx !== -1) {
return squares[lines[successIdx][0]];
}
return null;
}
handleClick(i) {
const history = this.state.history;
const squares = history[history.length - 1].slice();
if (squares[i] || this.calculateWinner(squares)) {
return;
}
squares[i] = this.state.xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O';
this.setState({
xIsNext: !this.state.xIsNext,
history: history.concat([squares]),
});
}
jump(idx) {
// 引用类型创造新引用赋值,触发更新
this.setState({
history: this.state.history.slice(0, idx + 1)
});
}
render() {
const history = this.state.history;
const squares = history[history.length - 1];
const winner = this.calculateWinner(squares);
let status = winner ? `winner:${winner}` : `Next player: ${this.state.xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O'}`;
return (
<div className="game">
<div className="game-board">
<Board handleClick={(i) => this.handleClick(i)} squares={squares}/>
</div>
<div className="game-info">
<div className="status">{status}</div>
<ol>
{history.map((item, idx) => (
<li key={idx}>
<button onClick={() => this.jump(idx)}>{winner && idx === history.length - 1 ? `winner:${winner}` : `next: ${idx % 2 === 0 ? 'X' : 'O'}`}</button>
</li>
))}
</ol>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
// ========================================
// react组件上树
ReactDOM.render(
<Game />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
# jsx规则
jsx(javascript XML)
- 换行html片段加括号
- 混入
js表达式用花括号一个表达式可以产生一个具体的值
- jsx只能有一个根标签
- 标签必须闭合
<hr/>1 - 不要自定义标签
- 组件标签首字母大写
- class换
chassName - style写对象形式,并且属性名转小驼峰:
const VDOM = (<h1 style={{backgroundColor: 'red'}}>Hello React!</h1>);1 - style写大部分数字不用加px,
lineHeight需要const VDOM = (<h1 style={{height: 100}}>Hello React!</h1>);1
- 注释写法
const VDOM = ( <h1 style={{backgroundColor: 'red'}}> {/* <hr/> */} Hello React! </h1> );1
2
3
4
5
6
# 条件渲染
- jsx语句返回
false会被忽略 - 所以可以用 && 表达式做条件渲染
false不是falsy,falsy会返回<div>0</div>
const { useState, useEffect } = React;
function MyApp() {
const [time, setTime] = useState(new Date());
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setInterval(() => setTime(new Date()), 1000);
return () => {
clearInterval(timer);
};
}, []);
return (
<div>
{time.getSeconds() % 2 === 0 && time.toLocaleTimeString()}
{/* 以下的falsy会显示 0 */}
{/* time.getSeconds() % 2 && time.toLocaleTimeString() */}
</div>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- 组件render方法直接返回null会不渲染此组件
const { useState, useEffect } = React;
const Child = props => props.show ? (<div>子组件</div>) : null;
function MyApp() {
const [show, setShow] = useState(true);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setShow(!show)}>toggle</button>
<Child show={show} />
</div>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 循环渲染
- 列表用map等将数据转化成jsx模板语法
- 列表需要加一个唯一的key值,帮助diff算法优化速率
const arr = ['张莎', '李四', '王五'];
const VDOM = (
<h1>
{ arr.map(item => <div key={item}>{ item }</div>) }
</h1>
);
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.getElementById('app'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
- 用setState时应该操作新的数组,不能修改原数组
- 删除传参可以用
箭头函数和bind - 数组增删改查不可变数据操作可以用:
- val.
concat(addVal) - [...val, addVal]
- val.
filter((item, idx) => idx !== delIdx) Array.from(val)Array.of(...val)entries/keys/values
- val.
- 对象增删改查可用:
- Object.
assign({}, info, {age: 18}) - {...info, age: 18}
- Object.
class MyApp extends React.Component {
state = {
friends: [
'小黄',
'小张',
'小李',
]
}
delete = idx => {
const newFriends = this.state.friends.filter((_, i) => i !== idx);
this.setState({ friends: newFriends });
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{
this.state.friends.map((item, idx) => {
return (
<li key={item}>
<span>姓名:{item}</span>
<button onClick={this.delete.bind(this, idx)}>删除</button>
{/* <button onClick={() => this.delete(idx)}>删除</button> */}
</li>
)
})
}
</ul>
)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 表单控制
- 在处理表单数据时,通过
state来关联表单数据的方式叫做受控组件 - 通过
ref来获取DOM元素的情况叫做非受控组件
- select组件的value可以接收数组,作为多个值
const { useState, useEffect } = React;
function MyApp() {
const selection = [
'北京',
'上海',
'广州',
'深圳',
];
const [val, setVal] = useState([]);
const changeVal = e => {
setVal(val.includes(e.target.value) ?
val.filter(item => item !== e.target.value)
: [...val, e.target.value]);
};
return (
<div>
<select value={val} onChange={changeVal} multiple={true}>
{selection.map(item => <option value={item} key={item}>{item}</option>)}
</select>
</div>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 可以用一个name属性来区分,然后用同一个函数来处理数据变化
function MyApp() {
const [data, setData] = useState({
account: '',
pwd: '',
});
const changeVal = e => {
setData(Object.assign({}, data, {
[e.target.name]: e.target.value
}))
}
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={data.account} onChange={changeVal} name="account" />
<input type="text" value={data.pwd} onChange={changeVal} name="pwd" />
<div>账号:{data.account}</div>
<div>密码:{data.pwd}</div>
</div>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 在 React 中,
<input type="file" />始终是一个非受控组件,因为它的值只能由用户设置,而不能通过代码控制。
<input type="file" />
1
# 类式组件
- 类组件继承
React.Component构造react组件,实现render方法生成dom节点
<script type="text/babel">
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
title: '你好啊大兄弟!'
};
}
render() {
return (<h1>{this.state.title}</h1>);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById('app'));
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 类组件控制state要注意:
- this的控制:事件触发时this是否正确(用箭头函数或bind解决)
- 修改状态时用
setState进行赋值,让dom进行触发响应式
- 事件绑定用驼峰,react重写了
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
isHot: false,
}
toggleState = () => {
this.setState({
isHot: !this.state.isHot,
})
}
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state;
return (<h1 onClick={this.toggleState}>今天天气好{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}啊!</h1>);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 利用科里化,减少函数入参,达到一个函数双向绑定多个input输入框的效果
class Login extends React.Component {
state = {
account: '',
pwd: ''
}
login = () => console.log(`用户名:${this.state.account},密码:${this.state.pwd}`);
saveState = (key) => (e) => this.setState({[key]: e.target.value});
render() {
const {account, pwd} = this.state;
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={account} onChange={this.saveState('account')} />
<input type="text" value={pwd} onChange={this.saveState('pwd')} />
<button onClick={this.login}>登录</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- props使用注意事项:
- props是只读属性,如果要做操作,先解构出来。
class People extends React.Component {
render() {
let { age } = this.props;
age = +age + 1;
return <h1>年龄:{age}</h1>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<People age="22"/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 批量传递,解构语法
class People extends React.Component {
render() {
let { name, age, sex } = this.props;
return (
<h1>
<div>姓名:{name}</div>
<div>年龄:{age}</div>
<div>性别:{sex}</div>
</h1>
)
}
}
const people = {
name: 'hdy',
age: 18,
sex: '男'
};
ReactDOM.render(<People {...people}/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 需要修改部分props,其余原样传下去时:
const Button = props => {
const { kind, ...other } = props;
const className = kind === "primary" ? "PrimaryButton" : "SecondaryButton";
return <button className={className} {...other} />;
};
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
- 官网 (opens new window)
- 引入
prop-types库 - 类
静态属性设置属性propTypes,限制类型 - 类
静态属性设置属性defaultProps,默认参数
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {}
}
MyComponent.propTypes = {
optionalArray: PropTypes.array,
optionalBool: PropTypes.bool,
optionalFunc: PropTypes.func,
optionalNumber: PropTypes.number,
optionalObject: PropTypes.object,
optionalString: PropTypes.string,
optionalSymbol: PropTypes.symbol,
// 任何可被渲染的元素(包括数字、字符串、元素或数组)
// (或 Fragment) 也包含这些类型。
optionalNode: PropTypes.node,
// 一个 React 元素。
optionalElement: PropTypes.element,
// 一个 React 元素类型(即,MyComponent)。
optionalElementType: PropTypes.elementType,
// 你也可以声明 prop 为类的实例,这里使用
// JS 的 instanceof 操作符。
optionalMessage: PropTypes.instanceOf(Message),
// 你可以让你的 prop 只能是特定的值,指定它为
// 枚举类型。
optionalEnum: PropTypes.oneOf(['News', 'Photos']),
// 一个对象可以是几种类型中的任意一个类型
optionalUnion: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.string,
PropTypes.number,
PropTypes.instanceOf(Message)
]),
// 可以指定一个数组由某一类型的元素组成
optionalArrayOf: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number),
// 可以指定一个对象由某一类型的值组成
optionalObjectOf: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.number),
// 可以指定一个对象由特定的类型值组成
optionalObjectWithShape: PropTypes.shape({
color: PropTypes.string,
fontSize: PropTypes.number
}),
// An object with warnings on extra properties
optionalObjectWithStrictShape: PropTypes.exact({
name: PropTypes.string,
quantity: PropTypes.number
}),
// 你可以在任何 PropTypes 属性后面加上 `isRequired` ,确保
// 这个 prop 没有被提供时,会打印警告信息。
requiredFunc: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
// 任意类型的必需数据
requiredAny: PropTypes.any.isRequired,
// 你可以指定一个自定义验证器。它在验证失败时应返回一个 Error 对象。
// 请不要使用 `console.warn` 或抛出异常,因为这在 `oneOfType` 中不会起作用。
customProp: function(props, propName, componentName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(props[propName])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
},
// 你也可以提供一个自定义的 `arrayOf` 或 `objectOf` 验证器。
// 它应该在验证失败时返回一个 Error 对象。
// 验证器将验证数组或对象中的每个值。验证器的前两个参数
// 第一个是数组或对象本身
// 第二个是他们当前的键。
customArrayProp: PropTypes.arrayOf(function(propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(propValue[key])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
})
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="./react/packages/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/prop-types@15.6/prop-types.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class People extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
age: PropTypes.number,
sex: PropTypes.string,
}
static defaultProps = {
sex: '男'
}
render() {
let { name, age, sex } = this.props;
return (
<h1>
<div>姓名:{name}</div>
<div>年龄:{age}</div>
<div>性别:{sex}</div>
</h1>
)
}
}
const people = {
name: 'hdy',
age: '18', // 类型错误
// sex: '男' // 使用默认
};
ReactDOM.render(<People {...people}/>, document.getElementById('root'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
官方建议少用ref,能提升效率
- 类式组件三种定义方式
- 字符串(官方说效率低)
- 回调形式
- createRef(官方推荐)
createRef是用
.current获取DOM
class MyInput extends React.Component {
input3 = React.createRef();
show1 = () => console.log(this.refs.input1.value);
show2 = () => console.log(this.input2.value);
show3 = () => console.log(this.input3.current.value);
render() {
return (
<h1>
<input ref="input1" onBlur={this.show1} placeholder="失去焦点提示"/>
<input ref={el => this.input2 = el} onBlur={this.show2} placeholder="失去焦点提示"/>
<input ref={this.input3} onBlur={this.show3} placeholder="失去焦点提示"/>
</h1>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyInput/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
React的自定义事件能做出更好的兼容性(IE9)
- React组件上声明的事件最终绑定到了
document这个DOM节点上,而不是React组件对应的DOM节点。故只有document这个节点上面才绑定了DOM原生事件,其他节点没有绑定事件。这样简化了DOM原生事件,减少了内存开销 - React以队列的方式,从触发事件的组件向父组件回溯,调用它们在JSX中声明的callback。也就是React自身实现了一套事件冒泡机制。event.stopPropagation()停止事件传播
- React有一套自己的
合成事件SyntheticEvent,不同类型的事件会构造不同的SyntheticEvent - React使用对象池来管理合成事件对象的创建和销毁,这样减少了垃圾的生成和新对象内存的分配,大大提高了性能
例:document内有100个onClick事件,但是统一收集在document上,事件冒泡机制,event.target又能拿到对应的元素,绑定的一个对应的方法,进行触发。完成事件代理。
createContext得到一个声明上下文的对象,祖先组件Provider进行向下穿透传递- 后代组件中需要使用的时候添加静态属性
contextType进行接收
开发一般不用,一般用来封装库
import React, { createContext } from 'react'
//声明context
const InfoCtx = createContext();
export default function Test() {
const { Provider } = InfoCtx;
const state = {
name: '爷爷给孙子',
age: 18
};
return (
<>
爷爷:{state.name}
<Provider value={state}>
<B />
</Provider>
</>
)
}
class B extends React.Component {
render() { return (<C />) }
}
class C extends React.Component {
static contextType = InfoCtx;
render() { return (<div>孙子:{this.context.name} - {this.context.age}</div>) }
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 函数式组件:从ctx对象拿出
Consumer,里面可以写函数,获得父组件传递的value
import React, { createContext } from 'react'
const InfoCtx = createContext();
const { Provider, Consumer } = InfoCtx;
// ...
function C() {
return (
<Consumer>
{val => <div>孙子:{val.name} - {val.age}</div>}
</Consumer>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 标签体内容,类似vue的
slot
import React from 'react'
import { NavLink } from 'react-router-dom'
export default function MyNavLink(props) {
const { children } = props;
return (
<NavLink activeClassName='haha' className="nav-class" {...props}>{children}</NavLink>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 使用
<MyNavLink to="/about">关于页面</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/test" children="测试页面" />
1
2
2
- 多个slot可以自定义名称,但只能以属性的方式传
<MyNavLink to="/test" left={<Back />} center={<Title />} right={<Selector />}/>
1
# 生命周期
挂载
constructor:(props) => void- static getDerivedStateFromProps:(props, state) => overwriteState
- render
componentDidMount
更新
- static getDerivedStateFromProps:(props, state) => overwriteState
shouldComponentUpdate: (nextProps, nextState) => boolean- render
getSnapshotBeforeUpdatecomponentDidUpdate
卸载
componentWillUnmount
错误处理
- static getDerivedStateFromError
componentDidCatch
- componentWillReceiveProps:在父组件更新props的时候调用
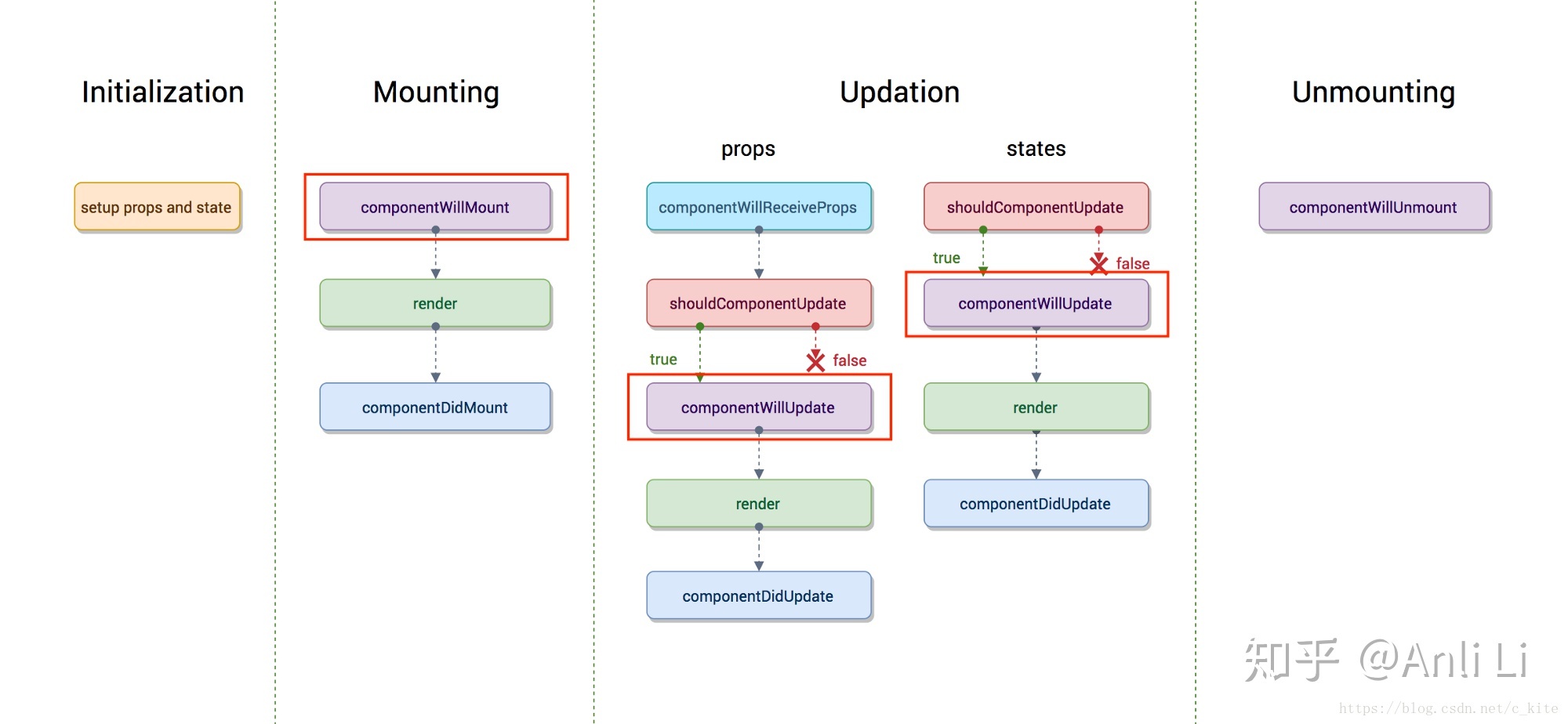
- 官网图 (opens new window)
- 删除:
componentWillMountcomponentWillUpdatecomponentWillReceiveProps
- 新增(很少用):
- static getDerivedStateFromProps
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
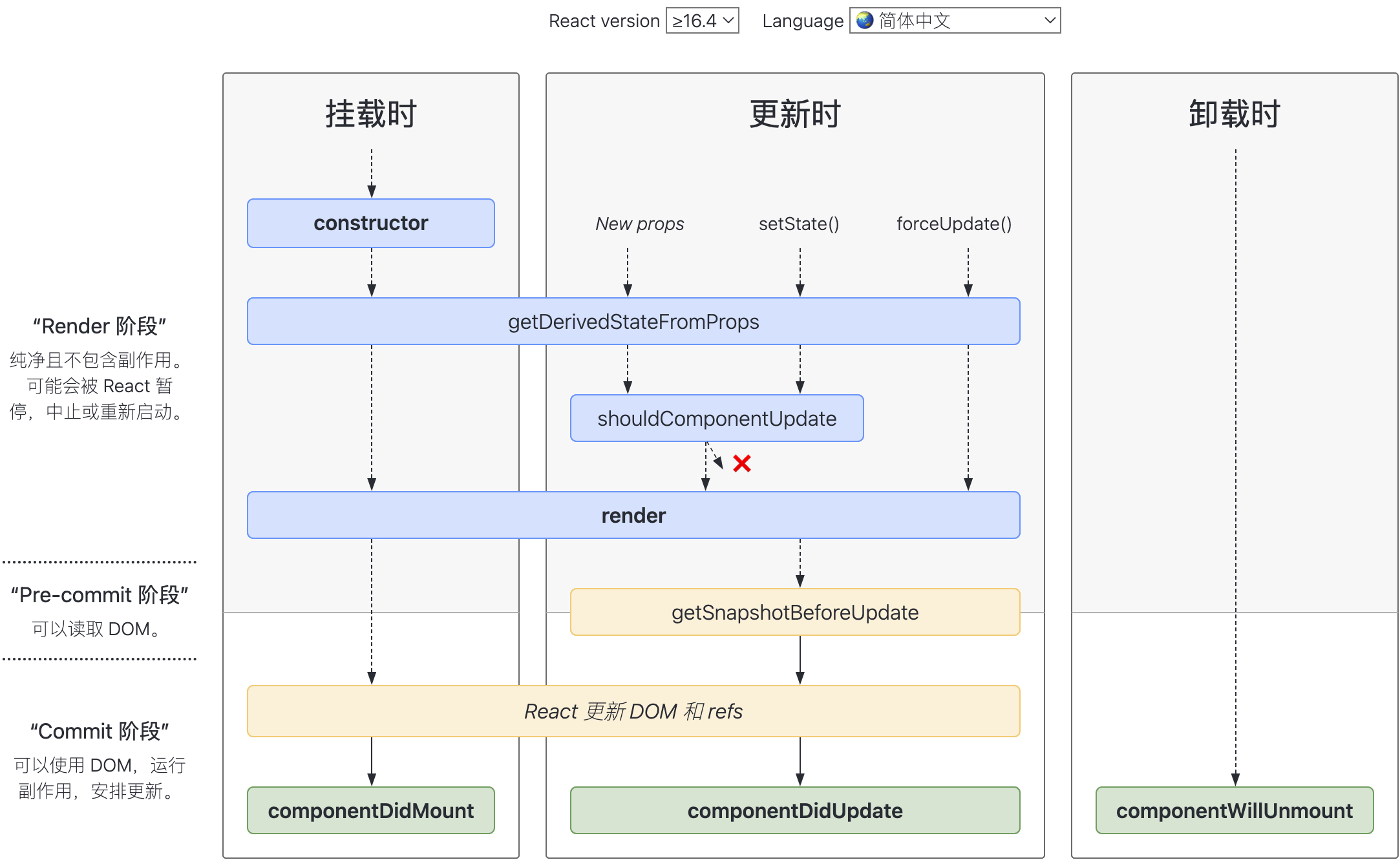
主要
8个钩子:5个常用的(粗体),三个不常用的
- 触发更新:
setState、props更新 - 强制更新:
forceUpdate
注:强制更新不触发
shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate: (nextProps, nextState) => booleangetSnapshotBeforeUpdate: (props, state) => payloadcomponentDidUpdate: (props, state, payload) => void
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate能够拿到改变前的状态快照,必须有返回值,传给componentDidUpdate的第三个参数。
要用getSnapshotBeforeUpdate必须要用componentDidUpdate。
class Login extends React.Component {
state = { num: 0 }
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.addOne}>+1</button>
{this.state.num}
</div>
)
}
// 每次点击依次触发:shouldComponentUpdate -> componentDidUpdate
addOne = () => this.setState({num: this.state.num + 1});
componentDidMount() {
// 只触发 componentDidUpdate
setInterval(() => {
this.forceUpdate();
}, 2000)
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');
return true;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate');
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
shouldComponentUpdate:(nextProps, nextState) => boolean- 返回boolean来确定是否更新
- forceUpdate可以绕过这个阀门强制更新
class Login extends React.Component {
state = { num: 0 }
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.addOne}>+1</button>
<button onClick={this.updateView}>更新视图</button>
{this.state.num}
</div>
)
}
// 点击状态+1了,但阀门阻止了视图更新
addOne = () => this.setState({num: this.state.num + 1});
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return false;
}
// 绕过阀门强制更新
updateView = () => this.forceUpdate()
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class Login extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
拜拜您嘞!
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('root'));
}, 2000)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('unmount');
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById('root'));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- Derived:衍生
- 本组件某个state完全依赖于外部props
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="./react/packages/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/babel.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class Father extends React.Component {
state = {
num: 0
}
addOne = () => this.setState({num: this.state.num + 1});
render() {
const { num } = this.state;
return (
<div>
爹: <button onClick={this.addOne}>+1</button>
<Child num={num}/>
</div>
)
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
return {money: props.num};
}
state = {
money: 0
}
render() {
return (
<div>
钱:{this.state.money}
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Father/>, document.getElementById('root'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
案例:不断地从上往下出新闻,同时保持当前阅读位置不变,就要在
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate拿到当前看的位置距离底部的距离,传给componentDidMount,让更新后这个数字保持不变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="./react/packages/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="./react/packages/babel.min.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.container {
width: 100px;
height: 150px;
background-color: rgb(250, 180, 134);
overflow: auto;
}
.news {
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
background-color: rgb(134, 204, 250);
margin-bottom: 3px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class News extends React.Component {
state = {
newsArr: [],
}
render() {
const { newsArr } = this.state;
return (
<div className="container" ref="container">
{newsArr.map(item => <div className="news" key={item}>{item}</div>)}
</div>
)
}
addNews = () => {
const { newsArr } = this.state;
const news = `新闻${newsArr.length + 1}`;
this.setState({
newsArr: [news, ...newsArr]
})
}
componentDidMount() {
// 不断地从上向下出新闻
this.timer = setInterval(this.addNews, 1000);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timer);
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
const container = this.refs.container;
const scrollBottom = container.scrollHeight - container.scrollTop;
return scrollBottom;
}
componentDidUpdate(_, __, oldscrollBottom) {
// 更新后保持距离底部距离不变
const { container } = this.refs;
container.scrollTop = container.scrollHeight - oldscrollBottom;
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<News/>, document.getElementById('root'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# HOC
- HOC:函数入参是一个组件,返回一个新的组件
- 可以做出mixin的效果,将原有组件进行扩展
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
// 原生组件
function NavBar(props) {
useEffect(() => {
console.log('NavBar componentWillMount');
}, []);
return (
<div>
<span>{props.left}</span>
<span>{props.center}</span>
<span>{props.right}</span>
</div>
)
}
// HOC:包装旧组件,生成新组件。可以附加很多功能,组件的mixin效果
function TypingTool(Comp, type) {
return function TypedTool(props) {
useEffect(() => {
console.log('wrapped componentWillMount');
}, []);
return (<Comp {...type} {...props} />)
}
}
const BackBar = TypingTool(NavBar, { left: "<" });
export default function App() {
return (
<div>
{<BackBar center="热销商品" right="···" />}
</div>
)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
- 利用
HOC思想,将render函数作为参数传入子组件内部,让组件自行决定渲染
const { useState, useEffect, useRef } = React;
function MyApp() {
return (
<>
<Mouse render={pst => <MovableCpm {...pst} />}
/>
</>
)
}
function MovableCpm(props) {
return (
<div style={{ position: 'absolute', left: props.x, top: props.y }}>
<div>当前位置是:{props.x}</div>
<div>当前位置是:{props.y}</div>
</div>
)
}
function Mouse(props) {
const [{ x, y }, setPosition] = useState({ x: 0, y: 0 });
useEffect(() => {
let timer;
const listener = e => {
if (timer) return;
timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
}, 40);
setPosition({
x: e.pageX,
y: e.pageY,
})
};
window.addEventListener('mousemove', listener);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', listener)
};
}, []);
return (
<>
<div>
<span>x:{x}</span>
<span>y:{y}</span>
</div>
{
props.render ? props.render({ x, y }) : false
}
</>
)
}
const container = document.getElementById('root');
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(container);
root.render(React.createElement(MyApp, null));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# Portals
- 可以实现挂载到React父组件以外的组件上去
const { useRef } = React;
function MyApp() {
return (
<div>
<span>儿子你好~</span>
{
ReactDOM.createPortal(<span>你好,我不是你儿子</span>, document.querySelector('#port'))
}
</div>
)
}
const container = document.getElementById('root');
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(container);
root.render(React.createElement(MyApp, null));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 合成事件会传播给React的父元素
- 浏览器事件会传播到DOM节点的父元素
const { useState, useRef } = React;
function MyApp() {
const [num, setNum] = useState(0);
const add = () => setNum(num + 1);
return (
// SyntheticBaseEvent
<div onClick={e => console.log(e)}>
<span>num: {num}</span>
{
ReactDOM.createPortal(<button onClick={add}>加一</button>, document.querySelector('#port'))
}
</div>
)
}
// pointerEvent
document.querySelector('#port').addEventListener('click', e => console.log(e));
const container = document.getElementById('root');
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(container);
root.render(React.createElement(MyApp, null));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 使用规则
- props不可变
React.StrictMode下初始化会让组件执行两次,以此来更明显的发现副作用BUG
# 经验总结
useMemo直接导出变量比useState性能好,在高频触发的事件中算是性能优化的点
const useDivs = () => {
// 性能好
// const showRowDivs = useMemo(() => {
// const startIdx = getStartIdx();
// const endIdx = getEndIdx();
// return calendars.slice(startIdx, endIdx);
// }, [calendars, horContainerWidth, scrollLeft, calendarGranularity, offsetTableUnit, DEFAULT_CEIL_WIDTH]);
// 性能比较差
const [showRowDivs, setShoeRowDivs] = useState<TwGanttCalendarVirtualBgcParams[]>([]);
useEffect(() => {
const startIdx = getStartIdx();
const endIdx = getEndIdx();
setShoeRowDivs(calendars.slice(startIdx, endIdx));
}, [calendars, horContainerWidth, scrollLeft, calendarGranularity, offsetTableUnit, DEFAULT_CEIL_WIDTH]);
return {
showRowDivs
};
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
