# 第1节 介绍
- vue3使用monorepo形式来管理源代码。优势是多个包本身逻辑独立,可以拥有自己的单元测试等。
- 全部使用typescript重写,vue2使用flow类型检测
- vue3使用proxy来进行数据劫持:vue2的defineProperty新增数据是不能进行监听,要用
Vue.$set(key, val)的形式 - 编译优化:生成
Block tree,slot优化、diff算法优化 - 从
options API到Composition API:options API在代码内配置的较分散,methods、生命周期等等,Composition API代码逻辑放到一处,易于管理和理解 - 多个组件共享逻辑:Vue2使用
mixin,Vue3使用hooks,将代码抽离出去,可以共享,并且还是响应式的。 - 删除了一些不常用的方法
filter...
- CDN引入
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `<div>hello vue3</div>`
})
app.mount('#app');
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- 原生实现计数器
<body>
<button class="reduce">-</button>
<span class="num">0</span>
<button class="add">+</button>
<script>
const reduce = document.querySelector('.reduce');
const add = document.querySelector('.add');
const proxy = new Proxy({ num: 0 }, {
set(target, key, val) {
if (key === 'num' && val >-1 && val < 100) {
target[key] = val;
const numEle = document.querySelector('.num');
numEle.innerText = val;
}
}
})
add.addEventListener('click', () => proxy.num++);
reduce.addEventListener('click', () => proxy.num--);
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- VUE写法
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<button @click="decre">-</button>
<span>{{count}}</span>
<button @click="incre">+</button>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
incre() {
this.count++;
},
decre() {
this.count--;
},
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- template如果以#开头,会被
document.querySelector处理
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="x-template" id='temp'>
<h2>哈哈</h2>
<span>{{msg}}</span>
</script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello vue3!'
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- html原生
template,不会被渲染的一类元素,提供给JS处理的html模板
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id='temp'>
<h2>呵呵</h2>
<span>{{msg}}</span>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello vue3!'
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- vue3中this是谁?
本组件实例的proxy对象,
instance.proxy。methods方法和生命周期函数用bind返回了一个绑定好this的函数,执行的时候实际上就是执行的绑定后的函数。
- vue3官方文档说methods不能使用箭头函数,那么用箭头函数this是谁?为什么?
window。箭头函数不绑定this,直接使用
上层作用域this,vue定义时上层this就是window
- 源码调试
- 第一节,1:56:00
- github:
vue-next
- UI组件库:Element-plus、antdesign Vue
# 第2节 class/style绑定
- 动态绑定
class名和展示判断
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id='temp'>
<div :class="{ [title]: isActive}">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<style>
.active {
color: red;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
title: 'active',
isActive: true
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id='temp'>
<div :class="className">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<style>
.active {
color: red;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
title: 'active',
isActive: true
}
},
computed: {
className() {
return { [this.title]: this.isActive }
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 字符串就是类名
- 变量取
data或computed数据 - 也可以
三元表达式取结果 - 还可以嵌套写对象语法
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id='temp'>
<div :class="['abc', title, isActive ? 'active' : '', { active: isActive }]">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<style>
.active {
color: red;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
title: 'hdy',
isActive: true
}
},
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- 支持对象写法和数组写法
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id='temp'>
<div :style="{color: 'red', backgroundColor: bgc}">你好哈哈哈</div>
<div :style="[bgObj1, bgObj2]">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
bgc: 'blue',
bgObj1: {
backgroundColor: 'black',
color: 'white'
},
bgObj2: {
fontSize: '30px'
}
}
},
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- 直接使用
v-bind=""可以将整个对象的键值对作为属性的键值对绑定上去
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div name="hdy" age="18">你好哈哈哈</div>
<div v-bind="me">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
me: {
name: 'hdy',
age: "18"
}
}
},
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- 多个事件的绑定用
v-on="{}"语法
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div v-on="{ click: say, mousemove: go }">你好哈哈哈</div>
</template>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 1px #333;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
methods: {
say() {
console.log('鼠标点击了');
},
go() {
console.log('鼠标移动了')
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 第3节 条件渲染/diff算法
- 输入分数判断及格
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>
<input type="number" v-model="score">
<div v-if="score > 89">优秀</div>
<div v-else-if="score > 59">及格</div>
<div v-else>不及格</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
score: 100
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
v-for遍历对象,一个参数是value,多个参数是(value, key, index)- v-for遍历数字,从1开始,到n,多个参数是(num, index)
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div v-for="(value, key) of obj">{{key}}:{{value}}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
obj: {
name: 'hdy',
age: 18
}
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- diff算法:1:20:00
- 新旧虚拟dom从头开始比较,到不同的地方跳出while循环
- 从尾部开始比较,到不同跳出while循环
- 拿到新旧dom不同的下标值,做比较,多出来的
mount,少了就unmount,更新就update - 如果遇到中间还有很多无序的下标,用一个数组记录key值,尽可能的复用原有节点,进行tagName比较,后进行对应节点的移动更新,最大程度的复用原节点
- 结论:唯一的key是十分必要的
- 没有key,就尽可能的复用节点,更新内容,从头开始遍历、从尾开始遍历,相同元素深度比较,更新DOM
- 性能优化:
条件渲染的空标签用
template替代div,可以少渲染一个节点,性能优化。类似小程序的block。
注:v-show不支持template
# 第4节 watch/基础案例
- 模板语法缺点:
- 大量复杂逻辑,不便维护
- 当有多次同样逻辑,存在重复代码
- 没有缓存,重复计算
- computed就能够解决这些问题。
- 书写的
computed属性是以getter、setter的形式挂载到instance.proxy上面的 - 简写可以写做单个函数的形式,隐式转化为
getter
- 书写的
- 监听某个数据改变,要做一系列操作时用watch,如网络请求,就不适合用computed
- [key: string]: Function | Object | String【meghods里面定义的方法名】 | Array【多个函数或配置逐一被调用】
- 深度监听:默认不是深度监听的,需要深度监听
deep:true - 立即执行:默认只有监听到发生改变了才会执行,一开始并不会执行,可以设置
immediate: true来立即执行一次 - 监听对象某个属性:
"info.name"
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="me.name">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data() {
return {
me: {
name: 'hdy',
age: 18
}
}
},
watch: {
me: {
handler(newName, oldName) {
console.log('watch');
},
deep: true
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- data内一个对象中或数组中的某一个属性
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<button @click="changeName">深度修改</button>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
friends: [ {name: '张三'}, {name: '李四'} ]
}
},
methods: {
changeName() {
this.friends[0].name = '王五';
}
},
watch: {
['friends.0.name']() {
console.log('---');
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 生命周期中用$watch去侦听,返回值是一个本watch的取消器
两秒失效的侦听器
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>{{friends[0].name}}</div>
<button @click="changeName">深度修改</button>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
friends: [ {name: '张三'}, {name: '李四'} ]
}
},
methods: {
changeName() {
this.friends[0].name += '哈';
}
},
created() {
const unwatch = this.$watch(
'friends',
() => console.log('侦听到了'),
{ deep: true }
)
setTimeout(() => unwatch(), 2000);
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
- 商品的增删改查
- 注意v-for和v-if的
嵌套关系
<body>
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
border: 1px solid gray;
margin: 0 auto;
}
tr {
height: 50px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: top;
}
td, th {
padding: 0 10px;
border: 1px solid gray;
min-width: 100px;
max-width: 200px;
}
th {
background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238);
color:rgb(88, 88, 88);
line-height: 50px;
}
button {
margin-right: 5px;
}
button:last-child {
background-color: rgb(253, 197, 197);
}
input {
margin: 5px 10px;
line-height: 30px;
max-width: 100px;
}
div {
margin-left: 30px;
}
</style>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<table>
<thead>
<th>编号</th>
<th>书籍</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>操作</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><input type="text" v-model="id"></td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="name"></td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="price"></td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="num"></td>
<td><button @click="newGood">添加</button></td>
</tr>
<template v-for="(item, idx) of goods">
<tr v-if="+item.num > 0" :key="item.id">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>{{item.num}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="decre(idx)">-</button>
<button @click="incre(idx)">+</button>
<button @click="del(idx)">删</button>
</td>
</tr>
</template>
</tbody>
</table>
<div>总价:{{ total }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
id: '',
name: '',
price: '',
num: '',
goods: [{
id: 0,
name: '《你不知道的JS》',
price: 100,
num: 1
},
{
id: 1,
name: '《JS语言精粹》',
price: 200,
num: 2
},
]
}
},
computed: {
total() {
return this.goods.reduce((pre, item) => pre + (+item.price * +item.num), 0);
}
},
methods: {
decre(idx) {
const goods = this.goods;
this.goods[idx].num = goods[idx].num > 0 ? goods[idx].num - 1 : goods[idx].num;
},
incre(idx) {
const goods = this.goods;
this.goods[idx].num = goods[idx].num < 99 ? goods[idx].num + 1 : goods[idx].num;
},
del(idx) {
const goods = this.goods;
this.goods.splice(idx, 1);
},
newGood() {
const newGood = {
id: this.id,
name: `《${this.name}》`,
price: +this.price,
num: +this.num,
}
this.goods.push(newGood);
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
# 第5节 v-model
v-model只是v-bind和v-on的语法糖
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<input type="text" :value="msg" @input="msg = $event.target.value">
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
msg: ''
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- 加
lazy只是改变了监听的事件,改为change
export const vModelText: ModelDirective<
HTMLInputElement | HTMLTextAreaElement
> = {
created(el, { modifiers: { lazy, trim, number } }, vnode) {
el._assign = getModelAssigner(vnode)
const castToNumber =
number || (vnode.props && vnode.props.type === 'number')
addEventListener(el, lazy ? 'change' : 'input', e => {
if ((e.target as any).composing) return
let domValue: string | number = el.value
if (trim) {
domValue = domValue.trim()
} else if (castToNumber) {
domValue = toNumber(domValue)
}
el._assign(domValue)
})
if (trim) {
addEventListener(el, 'change', () => {
el.value = el.value.trim()
})
}
if (!lazy) {
addEventListener(el, 'compositionstart', onCompositionStart)
addEventListener(el, 'compositionend', onCompositionEnd)
// Safari < 10.2 & UIWebView doesn't fire compositionend when
// switching focus before confirming composition choice
// this also fixes the issue where some browsers e.g. iOS Chrome
// fires "change" instead of "input" on autocomplete.
addEventListener(el, 'change', onCompositionEnd)
}
},
// set value on mounted so it's after min/max for type="range"
mounted(el, { value }) {
el.value = value == null ? '' : value
},
beforeUpdate(el, { value, modifiers: { lazy, trim, number } }, vnode) {
el._assign = getModelAssigner(vnode)
// avoid clearing unresolved text. #2302
if ((el as any).composing) return
if (document.activeElement === el) {
if (lazy) {
return
}
if (trim && el.value.trim() === value) {
return
}
if ((number || el.type === 'number') && toNumber(el.value) === value) {
return
}
}
const newValue = value == null ? '' : value
if (el.value !== newValue) {
el.value = newValue
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
- 将数组对应多个checkbox
- 必须要有value,
$event.target.value才能正确的跟踪值 label里的for对应input里的id
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>
<label for="红宝书">红宝书
<input type="checkbox" v-model="books" value="红宝书" id="红宝书">
</label>
</div>
<div>
<label for="绿宝书">绿宝书
<input type="checkbox" v-model="books" value="绿宝书" id="绿宝书">
</label>
</div>
<div>
<label for="蓝宝书">蓝宝书
<input type="checkbox" v-model="books" value="蓝宝书" id="蓝宝书">
</label>
</div>
<div>{{ books }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
books: [],
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
- 单选框,值唯一
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>
<label for="male">male
<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="male" id="male">
</label>
</div>
<div>
<label for="female">female
<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="female" id="female">
</label>
</div>
<div>性别是:{{ sex }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
sex: '',
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<select v-model="current">
<option v-for="city of cities" :value="city">{{ city }}</option>
</select>
<div>当前在:{{ current }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
cities: [ '北京', '上海', '深圳'],
current: '上海',
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- 如果要展示多个,数值变成数组。按住command多选。
- mutiple:多选
- size:展示个数
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<select v-model="current" multiple size="4">
<option v-for="city of cities" :value="city">{{ city }}</option>
</select>
<div>当前在:{{ current }}</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
data() {
return {
cities: [ '北京', '上海', '深圳'],
current: ['上海', '深圳'],
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- lodash库:封装一些好用的方法
# 第6节 组件化
- 一般组件取名方式:
- 短横线分割符 ( 推荐 ) :
'my-comp' - 驼峰(只有在脚手架有效):
'MyComp'
- 短横线分割符 ( 推荐 ) :
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>我是爸爸</div>
<com-a></com-a>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
})
const child ={
template: '<div>我是子组件</div>'
}
app.component('com-a', child);
app.mount('#app');
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<template id="temp">
<div>我是爸爸</div>
<com-a></com-a>
<com-a></com-a>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const child ={
template: '<div>我是子组件</div>'
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: '#temp',
components: {
'com-a': child,
}
});
app.mount('#app');
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 第7节 webpack-loader
- webpack is a static module bundler for modern jsvascript application.
- webpack是一个服务于现代javascript应用程序的
静态的模块化打包工具。 - 将各种资源的语法打包成 浏览器认识的 html/css/图片/视频等格式。
- 安装
npm i webpack webpack-cli -g
webpack --version
2
3
- 打包体验
// test/src/esm.js
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
export { a, b }
2
3
4
// test/src/cmjs.js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
module.exports = {
add
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
// test/src/index.js
import { a, b } from './esm';
const { add } = require('./cmjs');
console.log(add( a, b ));
2
3
4
5
test/index.html
<body>
<script src="./dist/main.js"></script>
</body>
2
3
- test目录下执行命令,后就能看结果
webpack
- 依赖管理:
package.json - 开发依赖:直接
install - 生产依赖:
install --save--dev,简写install -D - 默认入口:当前文件夹下的src下的
index文件,根据这个文件去寻找其他依赖,生成依赖关系图,进行打包
npm初始化:
npm init -y
- 使用本地webpack两种方法:
- npx
npm install webpack webpack-cli -D npx webpack1
2
3- 或者直接在package.json创建脚本
"scripts": { "build": "webpack" }1
2
3
自定义入口/出口
npx webpack --entry ./src/index.js --output-path ./build
- 默认的配置文件是当前项目根目录的
webpack.config.js
const path = require("path");
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/index.js",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "build"),
filename: "bundle.js",
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 输出路径必须是绝对路径,
__dirname是当前文件所在路径
- loader可以对不同的源代码进行解析,打包对应的文件,如:css-loader、ts-loader
npm i css-loader -D
npm i style-loader -D
2
- 使用方式(2种):
- 内联
import 'css-loader!./src/css/style.css'1- 配置(常用)
有多个loader就用use配置数组。
注:use的执行顺序是 倒序 的,最下面的loader先执行。css文件需要先css-loader解析,再style-loader插入到文件内去//webpack.comfig.js module.exports = { // ... module: { rules: [ { test: /\.css$/, // loader: "css-loader", // use: [ {loader: "css-loader", options: xxx} ] use: [ "style-loader", "css-loader" ] } ] } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 进行一些CSS适配,将CSS转换成各浏览器都能识别的状态。如:加前缀、#12345678透明度等。
npm i postcss-loader -D
npm i autoprefixer -D
2
rules: [
{
test: /\.(css|less)$/,
use: [
"style-loader",
"css-loader",
{
loader: "postcss-loader",
options: {
postcssOptions: {
plugins: [
require("autoprefixer"),
]
}
}
},
"less-loader",
]
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- 或者直接使用已经配置好的
postcss-preset-env插件配置,会将大多数样式转化成各浏览器适配的版本。
rules: [
{
test: /\.(css|less)$/,
use: [
"style-loader",
"css-loader",
{
loader: "postcss-loader",
options: {
postcssOptions: {
plugins: [
require("postcss-preset-env"),
]
}
}
},
"less-loader",
]
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- 对应
file-loader
npm i file-loader -D
rules: [
{
test: /\.(jpe?g|gif|svg|png)$/,
loader: "file-loader"
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
- 使用
url-loader,与file-loader相似,但是可以将较小的图片转化成base64格式,性能优化
- placeholder:
- [ext] :处理文件的扩展名
- [name] : 处理文件的原名称
- [hash] :哈希值,文件内容
- [path] :文件相对于webpack.config.js文件的相对路径
- [hash:【length】] :哈希截取长度
- [contentHash]:
{
test: /\.(png|gif|svg)$/,
use: {
loader: "file-loader",
options: {
outputPath: "img",
name: "[name]_[hash:6][ext]"
}
},
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
asset module type:webpack5推出的统一静态资源打包方法- 配置项:
- asset/resource:类似file-loader
- asset/inline:类似url-loader
- asset/source:类似原row-loader
- asset:选择导出配置项
{
test: /\.(png|gif|svg)$/,
type: "asset/resource",
}
2
3
4
{
test: /\.(jpe?g|png|gif|svg)$/,
type: "asset",
parser: {
dataUrlCondition: {
maxSize: 100 * 1024,
}
},
generator: {
filename: "img/[name]_[hash][ext]"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 字体、icon、font打包:
file-loader/asset/resource - plugin和loader区别:
- 添加功能:plugin
- 模块打包:loader
# 第8节 webpack-plugin
CleanWebpackPlugin:自动清理原打包文件
npm i clean-webpack-plugin -D
const { cleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin()
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
HtmlWebpackPlugin:自动生成html入口文件
注意,导入没有解构!
npm i html-webpack-plugin -D
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "./public/index.html" // 可以指定模板
})
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DefinePlugin:注入全局变量
const { DefinePlugin } = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new DefinePlugin({
BASE_URL: "'./public/'"
})
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
- public文件夹下的东西会被直接复制到打包后的文件夹内,是因为有
CopyWebpackPlugin这个插件
npm i copy-webpack-plugin -D
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: 'public',
to: '',
globOptions: {
ignore: [
"**/index.html"
]
}
}
]
})
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
babel本质上是一个编译器,将我们的源代码转换成另一份源代码
- 安装
npm i @babel/core @babel/cli -D
npm i @babel/preset-env -D
2
- 常用ES6转ES5
npx babel src/test.js --out-dir ./ --presets=@babel/preset-env
- webpack内使用
npm i babel-loader @babel/core -D
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: [ "@babel/preset-env" ],
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 配置抽离:
- (荐)babel.config.js/json...
- babelrc.js/json
// webpack.config.js module.rules { test: /\.js$/, loader: "babel-loader", }1
2
3
4
5// babel.config.js module.exports = { plugins: [], presets: [ '@babel/preset-env' ] }1
2
3
4
5
npm i vue@next
npm i vue-loader@next -D
npm i @vue/compiler-sfc -D
2
3
// weboack.config.js
const { DefinePlugin } = require('webpack');
const { VueLoaderPlugin } = require('vue-loader/dist/index');
// plugins
plugins: [
// ..
new DefinePlugin({
BASE_URL: "'./public/'",
__VUE_OPTIONS_API__: true,
__VUE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__: true
}),
new VueLoaderPlugin()
]
// rules
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader'
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- vue/home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{ msg }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Vue!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
h2 {
color: red;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// index.js
const { createApp } = require('vue');
import home from'./vue/Home.vue';
const app = createApp(home);
app.mount("#app");
2
3
4
5
6
- index.html(模板)
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
2
3
- mode:
development开发模式,打包就不会压缩。打包上线设置production - devtool:
source-map,出现问题能够定位到源文件位置 - vscode调试插件:
vetur、volar(vue3支持较好)
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
devtool: "source-map",
}
2
3
4
- 编译器原理学习:简单的源码 (opens new window)
# 第9节 webpack-devServer
- 三种可选方式:
- webpack watch mode
//package.json "scripts": { "build": "webpack --watch" }1
2
3
4或者直接配置里面添加watc:true
// webpack.config.js module.exports = { // ... watch: true }1
2
3
4
5- webpack-dev-server(常)
实际上是webpack用express搭建的一个本地服务器,配上监听变化和自动编译操作。
且打包后并不写入文件,而是使用memfs库写入内存,在内存中进行调用,减少了写文件阶段,访问更为快速。npm i webpack-dev-server -D1//package.json "scripts": { "server": "webpack server" }1
2
3
4如果服务器没找到的资源,会从这里进行查找。
开发阶段用static,生产阶段用CopyWebpackPlugin将静态资源一起打包。// webpack.config.js module.exports = { // ... devServer: { static: "./public", } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7- webpack-dev-middleware
当前webpack-dev-server属于热加载
live-reloade,更改一个位置全部浏览器刷新HMR(hot module replace)
模块热替换是修改了哪个模块只热加载哪个模块,其他模块状态不变,就不会丢失掉当前测试的整个前端保存的状态。
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
target: "web",
devServer: {
static: "./abc",
hot: true,
},
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// aa.js
console.log('cdc');
let a = 110;
export default {
a
}
2
3
4
5
6
// index.js
import "./aa";
// 需要热加载模块
if (module.hot) {
// 第二个参数是热加载时的回调
module.hot.accept('./aa.js', () => console.log("aa.js模块更新了!"));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Vue-loader已自动支持模块热替换
- 模块热加载原理:webpack起了一个express静态资源服务器,起了一个socket长连接服务实时推送信息。
- 服务器监听到模块发生变化后,向客户端推送变化模块:(manifist.json 和 updata chunk),浏览器就能进行实时更新。
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
// ...
devServer: {
static: "./public",
hot: true,
host: "0.0.0.0", // 可以开启ipv4访问
port: 8888,
open: true, // 是否自动打开浏览器
compress: true, // 是否开启gzip压缩
proxy: { // 是否开代理,开发阶段有效
"/api": {
target: "http://localhost:8070",
pathRewrite: { "^/api": "" },
secure: false, // 是否阻止非https请求转发
changeOrigin: true, // 修改源,防数据服务器校验header
}
}
},
resolve: {
extensions: [ '.js', '.json', '.vue', '.ts' ], // 默认后缀名
alias: {
"@": path.resolve(__dirname, "./src"), // 设置路径别名
"js": path.resolve(__dirname, "./src/js"),
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 目录:将生产环境和开发环境做一个自定义配置,公公配置使用
webpack-merge来合并
config
|-webpack.comm.config.js
|-webpack.dev.config.js
|-webpack.prod.config.js
package.json
2
3
4
5
package.json
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --config ./config/webpack.prod.config.js",
"serve": "webpack serve --config ./config/webpack.dev.config.js"
}
2
3
4
webpack.comm.config.js
const path = require("path");
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
const { DefinePlugin } = require("webpack");
const { VueLoaderPlugin } = require('vue-loader/dist/index');
module.exports = {
target: "web",
entry: "./src/index.js",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "../build"),
filename: "js/bundle.js",
},
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".json", ".mjs", ".vue", ".ts", ".jsx", ".tsx"],
alias: {
"@": path.resolve(__dirname, "../src"),
"js": path.resolve(__dirname, "../src/js")
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ["style-loader", "css-loader", "postcss-loader"],
},
{
test: /\.less$/,
use: ["style-loader", "css-loader", "less-loader"],
},
// },
{
test: /\.(jpe?g|png|gif|svg)$/,
type: "asset",
generator: {
filename: "img/[name]_[hash:6][ext]",
},
parser: {
dataUrlCondition: {
maxSize: 10 * 1024,
},
},
},
{
test: /\.(eot|ttf|woff2?)$/,
type: "asset/resource",
generator: {
filename: "font/[name]_[hash:6][ext]",
},
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: "babel-loader"
},
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: "vue-loader"
}
],
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "./public/index.html",
title: "哈哈哈哈"
}),
new DefinePlugin({
BASE_URL: "'./'",
__VUE_OPTIONS_API__: true,
__VUE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__: false
}),
new VueLoaderPlugin()
],
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
webpack.dev.config.js
const { merge } = require('webpack-merge');
const commonConfig = require('./webpack.comm.config');
module.exports = merge(commonConfig, {
mode: "development",
devtool: "source-map",
devServer: {
static: "./public",
hot: true,
// host: "0.0.0.0",
port: 7777,
open: true,
// compress: true,
proxy: {
"/api": {
target: "http://localhost:8888",
pathRewrite: {
"^/api": ""
},
secure: false,
changeOrigin: true
}
}
},
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
webpack.prod.config.js
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require("clean-webpack-plugin");
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');
const {merge} = require('webpack-merge');
const commonConfig = require('./webpack.comm.config');
module.exports = merge(commonConfig, {
mode: "production",
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: "./public",
globOptions: {
ignore: [
"**/index.html"
]
}
}
]
}),
]
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 第10节 Vue-cli/vite
npm i @vue/cli -g
vue --version
# 升级
npm update @vue/cli -g
2
3
4
5
vue create myName
- 主要构成:
- 一个开发服务器(connect库),它基于 原生 ES 模块 提供了 丰富的内建功能,如速度快到惊人的 模块热更新(HMR)。
- 一套构建指令,它使用 Rollup 打包你的代码,并且它是预配置的,可输出用于生产环境的高度优化过的静态资源。
vite原理:构建自己的本地服务器,在服务器端将代码构建成浏览器能解析的es6代码,然后接受到请求时进行请求转发。
npm i vite -D
npx vite
2
3
- 直接就开启了本地服务,一般的打包功能都支持,已支持ts
使用第三方解析工具,如less、sass等,需要安装解析工具,不用配置
如:解析less
npm i less -D
npx vite
2
3
- 使用postcss对应插件
npm i postcss -D
npm i postcss-preset-env -D
2
postcss.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env'),
]
}
2
3
4
5
npx vite
vite有
预打包能力,所以会快, 预打包文件放在node_modules/.vite文件夹下
- 需要做对应的配置(vite.config.js)
npm i vue@next -D # vue
npm i @vitejs/plugin-vue -D # vite 解析vue语法
npm i @vue/compiler-sfc -D # .vue文件解析
2
3
// vite.config.js
const vue = require('@vitejs/plugin-vue');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
vue()
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
npx vite build
- 预览
npx vite preview --host
npm i @vitejs/create-app -g
create-app myName
cd myName
npm i
npm run dev
2
3
4
5
6
# 第11节 emit
- vue3定义组件可以有一个
emits属性,提前说好这个组件可以发射哪些事件
// .vue文件
export default {
emits: [ 'incre', 'decre' ],
methods: {
incre() {
this.$emit("incre");
},
decre() {
this.$emit("decre");
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 参数验证:emits可以写成对象的形式,给每个发射的事件进行参数验证
export default {
emits: {
incre(num) {
return num > 0;
},
decre(num) {
return num > 0;
}
},
methods: {
incre() {
this.$emit("incre", 1);
},
decre() {
this.$emit("decre", 1);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- 自己造轮子:tab-control
- 可以通过tab控制展示的局部内容
目录
components
|-TabControl.vue
App.vue
2
3
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<TabControl
:tabs="tabs"
@change-tab="changeTab"
:c-index="cIndex"
>
{{ contains[tabs[cIndex]] }}
</TabControl>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TabControl from "./components/TabControl.vue"
export default {
data() {
return {
tabs:[ '衣服', '鞋子', '裤子' ],
contains: {
'衣服': "啦啦啦衣服",
'鞋子': "啦啦啦鞋子",
'裤子': "啦啦啦裤子",
},
cIndex: 0
}
},
components: {
TabControl
},
methods: {
changeTab(idx) {
this.cIndex = idx;
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
<template>
<div>
<div class="tabs">
<div v-for="(tab, idx) of tabs"
:key="tab"
@click="changeTab(idx)"
class="tab"
:class="{ 'active': +cIndex === idx }"
>{{ tab }}
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<slot></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
emits: [ 'changeTab' ],
props: {
tabs: {
type: Array,
default: []
},
cIndex: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
},
methods: {
changeTab(idx) {
if (idx !== this.cIndex) {
this.$emit('changeTab', idx);
}
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.tabs {
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
display: flex;
}
.tab {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.tab.active {
color: rgb(250, 191, 191);
background-color: rgb(137, 182, 250);
}
.container {
margin-top: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 -3px 3px #333;
padding: 10px 5px;
height: calc(100vh - 50px);
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# 第12节 组件通信
- provide:父组件向所有的子孙组件提供参数
- inject:子孙组件需要使用祖先提供的参数时进行引入
- 按需inject,孙组件直接接收数据展示,子组件接收更改方法
注:要让inject参数变成响应式的,需要配置
app.config和注入computed
// main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App);
// 注入响应式参数配置,后续拿数据不用.value
app.config.unwrapInjectedRef = true;
app.mount('#app')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>爷爷的name: {{ name }}</div>
<child></child>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import child from "./components/Child";
import { computed } from 'vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
name: '爷爷'
}
},
components: {
child
},
provide() {
return {
name: computed(() => this.name),
changeName: this.changeName
}
},
methods: {
changeName(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
child.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>爸爸:<button @click="changeName('爸爸')">我要修改name</button></div>
<grandchild></grandchild>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import grandchild from './GrandChid.vue'
export default {
components: {
grandchild
},
inject: [ "changeName" ],
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
grandchild.vue
<template>
<div>
孙子:我拿到了name:{{ name }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inject: [ 'name' ]
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- github (opens new window)
- 取代vue2的全局事件总线
起步
npm i mitt
初始化
// utils/event_bus.js
import mitt from 'mitt';
const emitter = mitt();
export default emitter;
2
3
4
注册事件监听
<template>
<div>
<div>父组件的name: {{ name }}</div>
<child></child>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import child from "./components/Child";
import emitter from "./utils/event_bus";
export default {
data() {
return {
name: '爷爷'
}
},
components: {
child
},
created() {
emitter.on('changeName', (name) => this.changeName(name));
},
methods: {
changeName(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
触发事件
<template>
<div>
<div>子组件的按钮:<button @click="changeName('爸爸')">我要修改name</button></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import emitter from '../utils/event_bus';
export default {
methods: {
changeName(name) {
emitter.emit("changeName", name);
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 监听所有事件:
emitter.on("*", (type, ...args) => {})
- 取消
emitter.on('change', fn);
emitter.off('change', fn);
// 取消所有
emitter.all.clear();
2
3
4
5
父组件
<template>
<div>
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>
{{msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyInput from './components/myInput.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello',
}
},
components: {
MyInput
},
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
子组件
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" :value="modelValue" @input="change">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [ 'modelValue' ],
methods: {
change(e) {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', e.target.value);
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 子组件简写
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="myValue">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [ 'modelValue' ],
emit: [ 'update:modelValue' ],
computed: {
myValue: {
get() {
return this.modelValue;
},
set(newVal) {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', newVal)
}
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 绑定多个,需要给每个
v-model命名
父组件
<template>
<div>
<my-input v-model:msg="msg" v-model:title="title"></my-input>
<div>{{ title }}</div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyInput from './components/myInput.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello',
title: '这是title'
}
},
components: {
MyInput
},
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
子组件
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="myMsg">
<input type="text" v-model="myTitle">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [ 'msg', 'title' ],
computed: {
myMsg: {
get() {
return this.msg;
},
set(newVal) {
this.$emit('update:msg', newVal)
}
},
myTitle: {
get() {
return this.title;
},
set(newVal) {
this.$emit('update:title', newVal)
}
},
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 第13节 keep-alive/生命周期
- 动态组件的缓存,内部包裹的组件即使离开也不会销毁,会在后台运行
<keep-alive></keep-alive>
- include:String|Array|RegExp
- exclude:String|Array|RegExp
- max:Number|String
注:include是组件的
name属性
<keep-alive exclude = "SongsList,Home">
<router-view/>
</keep-alive>
2
3
- 异步加载的核心是Promise
import("../utils/math.js").then(({sum}) => sum(1, 2));
webpack通过JSONP的方式进行引入的
- 优势:打包时可以分包,首屏包更小,减少白屏时间
- Vue3中引入异步组件是通过
defineAsyncComponent来定义
const { defineAsyncComponent } from "vue";
const Home = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("../components/Home.vue"))
// 有参数
const Home = defineAsyncComponent({
loader: () => import("../components/Home.vue"),
loadingComponent: Loading,
delay: 1000, // 多久还没加载出来就展示loadingComponent组件
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 大部分业务都是用路由懒加载。特殊页面内异步组件可以这样定义。
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<TabControl
:tabs="tabs"
@change-tab="changeTab"
:c-index="cIndex"
>
<keep-alive>
<component :is="tabs[cIndex]"></component>
</keep-alive>
</TabControl>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TabControl from "./components/TabControl.vue";
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
const Home = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./components/Home.vue'));
const Categories = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./components/Categories.vue'));
const Me = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./components/Me.vue'));
export default {
data() {
return {
tabs:[ 'home', 'categories', 'me' ],
cIndex: 0
}
},
components: {
TabControl,
Home,
Categories,
Me,
},
methods: {
changeTab(idx) {
this.cIndex = idx;
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Home.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "主页"
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Categories.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "商品分类"
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Me.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "我的个人信息"
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
TabControl.vue(复用前面的分页Tab组件)
<template>
<div>
<div class="tabs">
<div v-for="(tab, idx) of tabs"
:key="tab"
@click="changeTab(idx)"
class="tab"
:class="{ 'active': +cIndex === idx }"
>{{ tab }}
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<slot></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
emits: [ 'changeTab' ],
props: {
tabs: {
type: Array,
default: []
},
cIndex: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
},
methods: {
changeTab(idx) {
if (idx !== this.cIndex) {
this.$emit('changeTab', idx);
}
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.tabs {
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
display: flex;
}
.tab {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.tab.active {
color: rgb(250, 191, 191);
background-color: rgb(137, 182, 250);
}
.container {
margin-top: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 -3px 3px #333;
padding: 10px 5px;
height: calc(100vh - 50px);
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
- 异步组件未展示的时候的应急方案,类似loading组件
- 默认展示default插槽
- 如果插槽组件加载中或未加载成功,就展示fallback插槽
<suspense>
<template #default>
<home />
</template>
<template #fallback>
<loading />
</template>
</suspense>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- keep-alive包裹的组件有
actived和deactived两个生命周期 - Vue3生命周期与Vue2相比,移除了
beforeDestroy、destroyed- 组件调用app.unmount()的时候,会触发
beforeUnmount、unmounted - 通过
emitter.on('name',fn)注册的事件可以在unmounted生命周期去emitter.off('name', fn)卸载
- 组件调用app.unmount()的时候,会触发
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "商品分类"
}
},
beforeCreate() { console.log('beforeCreate') },
created() { console.log('created') },
beforeUpdate() { console.log('beforeUpdate') },
updated() { console.log('updated') },
beforeMount() { console.log('beforeMount') },
mounted() {
console.log('mounted');
setTimeout(() => this.msg = '修改分类', 100);
},
beforeUnmount() { console.log('beforeUnmount') },
unmounted() { console.log('unmounted') },
activated() { console.log('activated') },
deactivated() { console.log('deactivated') }
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- Vue3移除了
$children属性。以下属性还可以用$refs$parent$root
# 第14节 动画
- 原理:transition检测有没有相关的类名,然后在恰当的时机把对应的类名添加到元素上
- 给单个组件/元素设置动画,可以使用transition API设置动画
- 六个类常用管理类
name-enter-from:进入前一帧初始化状态name-enter-to:进入后一帧目标状态name-leave-from:离开前一帧初始化状态name-leave=to:离开后一帧目标状态name-enter-active:进入的状态转变过程动画效果name-leave-active:离开的状态转变过程动画效果
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<transition name="hdy">
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'hello',
isShow: true,
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.hdy-enter-from,
.hdy-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.hdy-enter-to,
.hdy-leave-from {
opacity: 1;
}
.hdy-enter-active,
.hdy-leave-active {
transition: all 1s 200ms ease;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
- 自定义淡出方法
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<div class="box">
<transition name="hdy">
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "hello",
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
width: 100vw;
text-align: center;
}
.box > div {
margin: 0 auto;
}
.hdy-enter-active {
animation: bounce 1s ease;
}
.hdy-leave-active {
animation: bounce 1s ease reverse;
}
@keyframes bounce {
0% {
transform: scale(0);
}
50% {
transform: scale(1.2);
}
100% {
transform: scale(1);
}
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
- 首屏渲染是否需要动画:
:appear="true" - 如果要用生命周期调用js函数写动画,可以设置
css:false来关闭css动画检测,以及避免css动画影响效果 - 多个动画,animation和transion都有,那么都会生效。
- 可是如果多个动画时间不一样,以谁的时长为准?设置
type来告诉vue
- 可是如果多个动画时间不一样,以谁的时长为准?设置
<transtion name="myName" type="animation"></transtion>
- 设置
mode告诉vue多个动画的切换模式,如:两个元素切换展示,先进还是先出?- 默认同时动画
- in-out:先进后出
- out-in:先出后进
先进还是先出会决定布局的效果,因为先进的话布局并没有让出位置
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<div class="box">
<transition name="hdy">
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
<div v-else>{{ msg2 }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box2">
<transition name="hdy" mode="out-in" appear>
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
<div v-else>{{ msg2 }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "hello!",
msg2: "你好~",
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
width: 100vw;
text-align: center;
}
.box2 {
position: fixed;
text-align: center;
width: 100vw;
top: 50%;
}
.box>div,.box2>div {
margin: 0 auto;
}
.hdy-enter-active {
animation: bounce 1s ease;
}
.hdy-leave-active {
animation: bounce 1s ease reverse;
}
@keyframes bounce {
0% {
transform: scale(0);
}
50% {
transform: scale(1.2);
}
100% {
transform: scale(1);
}
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
- 一个第三方动画库,动画类名查找 (opens new window)
- 查找到对应的keyframes名,写进动画调用就行
npm i animate.css
// main.js
import "animation.css";
2
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<div class="box">
<transition name="hdy" mode="out-in">
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
<div v-else>{{ msg2 }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "hello!",
msg2: "你好~",
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
width: 100vw;
text-align: center;
}
.hdy-enter-active {
animation: fadeInDown 500ms ease;
}
.hdy-leave-active {
animation: fadeInDown 500ms ease reverse;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
- 或者可以直接传入类名
<transition
mode="out-in"
enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__rotateIn"
leave-active-class="animate__animated animate__rotateOut"
>
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
<div v-else>{{ msg2 }}</div>
</transition>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- transform动画也有生命周期钩子给我们使用
- 默认入参:enter(el, done) {}
<transition
mode="out-in"
enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__rotateIn"
leave-active-class="animate__animated animate__rotateOut"
@before-enter="beforeEnter"
@enter="enter"
@after-enter="afterEnter"
@enter-cancelled="enterCanceled"
@before-leave="beforeLeave"
@leave="leave"
@after-leave="afterLeave"
@leave-cancelled="leaveCancelled"
:css="false"
>
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
</transition>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 官网 (opens new window)
- the greensock animation platform,通过js设置css、svg、canvas等来控制动画
npm i gsap
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">切换</button>
<div class="box">
<transition
mode="out-in"
@enter="enter"
@leave="leave"
:css="false"
>
<div v-if="isShow">{{ msg }}</div>
</transition>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import gsap from 'gsap';
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "hello!",
isShow: true,
};
},
methods: {
enter(el, done) {
gsap.from(el, {
scale: 0,
y: 200,
onComplete: done
})
},
leave(el, done) {
gsap.to(el, {
scale: 0,
x: 200,
onComplete: done
})
},
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
width: 100vw;
text-align: center;
}
.hdy-enter-active {
animation: fadeInDown 500ms ease;
}
.hdy-leave-active {
animation: fadeInDown 500ms ease reverse;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
- 利用computed将数字的变化变成动态的
<template>
<div>
<button @click="add">切换</button>
<div>{{ showCount }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0,
showNum: 0
};
},
methods: {
add() {
this.count += 100;
}
},
computed: {
showCount() {
if (this.showNum === this.count) {
return this.showNum;
}
if(this.showNum < this.count) {
setTimeout(() => this.showNum++);
return this.showNum;
}
if(this.showNum > this.count) {
setTimeout(() => this.showNum--);
return this.showNum;
}
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
<template>
<div>
<button @click="add">切换</button>
<div>{{ showNum.toFixed(0) }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import gsap from 'gsap';
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0,
showNum: 0
};
},
methods: {
add() {
this.count += 100;
gsap.to(this, {
duration: 1,
showNum: this.count
})
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- transition-group来包裹一个动画组,组里面的里面的元素进出都可以实现相关的动画
<template>
<div>
<button @click="add">添加</button>
<button @click="del">删除</button>
<table>
<thead>
<th>id</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
</thead>
<transition-group tag="tbody" name="hdy">
<tr v-for="id of nums" :key="id">
<td>{{ id }}</td>
<td>张三</td>
<td>{{ id + Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) }}</td>
</tr>
</transition-group>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
nums: [0, 1, 2, 20, 30, 11]
};
},
methods: {
add() {
const index = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.nums.length);
const num = Math.floor(Math.random() * 30);
this.nums.splice(index, 0, num);
},
del() {
const index = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.nums.length);
this.nums.splice(index, 1);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.hdy-enter-from,
.hdy-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateX(50px);
}
.hdy-leave-to {
position: absolute;
}
.hdy-enter-active,
.hdy-leave-active {
transition: all 1s ease;
}
.hdy-move {
transition: all 500ms ease;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
margin: 0 auto;
}
tr {
height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: top;
}
td, th {
padding: 0 10px;
/* border: 1px solid gray; */
min-width: 50px;
}
th {
background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238);
color:rgb(88, 88, 88);
line-height: 50px;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
# 第15节 mixin/ConpositionAPI
- 定义:
export const mixinObj = {
create() {},
mounted() {},
data() {
return {
msg: ''
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 组件内混入:
mixin: [mixinObj]
- 全局混入:
const app = createApp(App);
app.mixin(mixinObj);
app.mount('#app');
2
3
- Vue3最大的写法转变就是
optionsAPI转化为compositionAPI - optionsAPI:同一个数据,逻辑分离,代码可读性还不够强
- CpmpositionAPI:setup函数,将同一
逻辑关注点合并,代码的变量函数名起的更见名知义,代码的可读性会很强。
setup里不能使用this,因为在
setup调用时,实例已经被创建,但是data/methods/等都还没有被解析
setup返回值:对象,可以在template中使用,替代原data的使用。如果data和setup中数据重了,用setup里面的。
入参context: { emit, slots, attrs }
数据需要用reactive函数将数组和对象包装成响应式数据。
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ state.count }}</div>
<button @click="decre">-</button>
<button @click="incre">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
count: 0
});
const incre = () => state.count++;
const decre = () => state.count--;
return {
state,
incre,
decre,
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
reactiveAPI只能包裹对象、数组解析成响应式数据,写起来比较麻烦refAPI可以处理值数据类型【String|Boolean|Number】,生成一个响应式对象,值存在对象.value里面。在模板里面使用时模板会自动解析ref.value
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="decre">-</button>
<button @click="incre">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let count = ref(0);
const incre = () => count.value++;
const decre = () => count.value--;
return {
count,
incre,
decre,
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- ref模板内是
浅层解包,如果把ref对象放到reactive对象内也可以解包,但放到一个普通对象内就不能解包,需要手动.value(一般也不这么用)。
- 值和对象的常量可以使用const修饰,但是const无法保证对象内部属性也不可变。
const obj = { name: '张三' };
// obj = {} // error
obj.name = '李四'; // 可以
2
3
- readonly可以设置对象内部的值也不可变。
原理是通过数据劫持,set的时候不修改值。
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ readonlyState.name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">试图修改名字</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { readonly } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const readonlyState = readonly({
name: 'hdy'
});
const changeName = () => readonlyState.name = '张三';
return {
readonlyState,
changeName
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- readonly可以让后面的值无法修改这个数据
- 本组件内部想要修改是可以的,就需要设置一个
reactive响应式的数据作为readonly的入参.
父组件
<template>
<div>
<home :readonlyMe="readonlyMe"></home>
<button @click="changeName">父组件改reactive数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, readonly } from 'vue';
import Home from './components/Home.vue';
export default {
setup() {
const me = reactive({ name: '父组件' });
const changeName = () => me.name = '爹改的';
// 给子组件的是不能改的数据,但是会接受到改变
const readonlyMe = readonly(me);
return {
me,
changeName,
readonlyMe
}
},
components: {
Home
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
子组件
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ readonlyMe.name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">子组件试图修改名字</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [ 'readonlyMe' ],
setup(props) {
let { readonlyMe } = props;
// 无效,因为爹给你的就是不能改的
const changeName = () => readonlyMe.name = '张三';
return {
readonlyMe,
changeName
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- readonly的ref定义相同,但是改值需要注意.value
const refName = ref("hdy");
const myChange = () => refName.value = '张三';
const readonlyName = readonly(refName);
// 无效
const change = () => readonlyName.value = '李四';
2
3
4
5
6
# 第16节 ConpositionAPI2
isProxy:是否为reactive或ref或readonly创建的proxyisReactive:是否为reactive创建的响应式代理isReadonly:是否是readonly创建的代理toRaw:返回响应式对象的原始对象shallowReactive:浅层响应式代理,只有本身一层是响应式的代理shallowReadonly:浅层的readonly对象,深层可以修改
isRef:判断当前数据是不是ref生成的响应式数据toRefs:将reactive对象进行结构,建立连接,解构后也是响应式的toRef:将reactive对象解构出某一个值,而并不是整个对象unref:将可能是ref对象的值解包,拿出.valueshallowRef:ref()也可能接收对象,并且也是深层响应式的,例如修改对象属性。如果只需要浅层响应式,只有修改value本身才响应式,就可以用shallowRef,性能会高一些triggerRef:shallowRef修改不会是响应式的,可以在修改后再用triggerRef强制响应式更新对应的相关数据customRef:自定义ref实现,例如防抖/节流
toRefs
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">修改name</button>
<button @click="changeName2">修改name2</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const me = reactive({ name: 'hdy' });
const { name } = toRefs(me);
// 作用相同
const changeName = () => name.value += 'y';
const changeName2 = () => me.name += 'y';
return {
name,
changeName,
changeName2
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
toRef
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">修改name</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRef } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const me = reactive({ name: 'hdy' });
const name = toRef(me, 'name');
const changeName = () => name.value += 'y';
return {
name,
changeName,
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
unref
<template>
<div></div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, unref, toRef } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const name = ref('hdy');
console.log(unref(name) === unref('hdy')); // true
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 自定义防抖ref
自定义ref的作用:
劫持DOM操作,进行数据的过滤类的自定义操作
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { customRef } from 'vue';
function debounceRef(value, delay) {
let timer = null;
return customRef((track, trigger) => (
{
get() {
track();
return value;
},
set(newVal) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
value = newVal;
trigger();
}, delay)
}
}
))
}
export default {
setup() {
let msg = debounceRef('', 500);
return {
msg
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
原理和vue2原理一样,只是写法不同。返回值本质是ref对象,修改也要用.value
- 写法一:传入getter函数
<template>
<div>
{{ dollor }}
<button @click="addOne">修改价格</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let price = ref(100);
const addOne = () => price.value++;
const dollor = computed(() => `$${ price.value }`)
return {
dollor,
addOne
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- 写法二:传入对象包含getter/setter
<template>
<div>
{{ dollor }}
<button @click="addOne">修改价格</button>
<button @click="addDollor">修改computed</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let price = ref(100);
const addOne = () => price.value++;
const dollor = computed({
get() { return `$${ price.value }`},
set() { addOne() }
})
const addDollor = () => dollor.value++;
return {
dollor,
addOne,
addDollor
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 监听数据变化
watchEffect:自动收集响应式依赖,默认刚开始一定会调用一次,来收集依赖- 入参1:(inValidate) => {},需要执行的函数
- 入参2:{ flush: 'post' },配置项。这个配置会在DOM挂载完再执行初始化
watch:需要手动收集依赖
watchEffect,不用告诉我监听谁,我自己知道。返回stop函数,调用就停止监听
<template>
<div>
{{ num }}
<button @click="changeNum">加一</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, watchEffect } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let num = ref(0);
const stop = watchEffect(() => {
console.log(num.value)
});
const changeNum = () => {
num.value++
if (num.value > 9) {
stop();
}
};
return {
num,
changeNum
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
入参fn的入参可以是一个清理函数,连续监听到变化,下一次变化可以清除上一次的侦听发起的无效操作,例如网络请求
<template>
<div>
{{ num }}
<button @click="changeNum">加一</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, watchEffect } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let num = ref(0);
watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
console.log(num.value);
const timer = setTimeout(() => console.log(`网络请求成功`), 1000);
onInvalidate(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
console.log('取消上个网络请求');
});
});
const changeNum = () => num.value++;
return {
num,
changeNum
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 用ref取元素/子组件
<template>
<div>
<h2 ref="title">hdy在学习Vue3</h2>
<button @click="show">查看value</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const title = ref(null);
const show = () => console.log(title.value); // h2元素
return {
title,
show
}
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- watch:
- 可以拿到变化前后的值
- 惰性,不会默认执行一次
- 需要告诉侦听的是谁
- 总结:
- 监听reactive/ref对象
watch(me, (newVal, oldVal) => {})1- 监听reactive对象的一个值
watch(() => me.name, (newVal, oldVal) => {})1- 侦听多个数据源,每个数据源改变都会触发
watch([() => me.name, age], (newVal, oldVal) => { console.log('侦听到了变化'); console.log(newVal); // ['hdyyyy', 21] })1
2
3
4- oldValue/newValue不想拿响应式对象:解构
watch(() => ({...me}), (newVal, oldVal) => {})1- 第三个参数,深度侦听、立即执行,
reactive对象默认deep为true
watch(me, (newVal, oldVal) => {}, { immediate: true, deep: true })1
2
3
4
侦听一个
ref值
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">改名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRef, watch } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const me = reactive({ name: 'hdy', age: 18 });
let name = toRef(me, 'name');
const changeName = () => name.value += 'y';
watch(name, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log('侦听到了变化');
console.log(oldVal + '->' + newVal);
})
return {
name,
changeName
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
侦听一个
reactive对象的一个值
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ me.name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">改名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRef, watch } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const me = reactive({ name: 'hdy', age: 18 });
const changeName = () => me.name += 'y';
watch(() => me.name, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log('侦听到了变化');
console.log(oldVal + '->' + newVal);
})
return {
me,
changeName
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- 基于watchEffect实现百度搜索的实时请求/取消请求
- 假如服务器响应时间是1s,那么在请求过程中用户继续输入关键字,就取消原先请求
server.js
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.listen('8888', () => console.log('listen 8888'));
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html')
const url = path.join(__dirname, './test.html');
const code = fs.readFileSync(url);
return res.send(code);
})
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
const query = req.query.s;
console.log(query);
setTimeout(() => res.send({data: query}), 1000);
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
test.html
不用v-model的原因是v-model监听的是input事件,中文输入法拼音时并不会触发,监听事件keyup就能很好的实时触发。
<body>
<div id="app">
<div><input type="text" @keyup="change"></div>
<h2>{{ search }}</h2>
<div>
<div v-for="ans of res" :key="ans">{{ans}}</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const { createApp, reactive, ref, watchEffect } = Vue;
const app = createApp({
setup() {
let search = ref('');
let res = ref([]);
watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
let controller = new AbortController();
const { signal } = controller;
fetch(`http://localhost:8888/search?s=${search.value}`, { signal })
.then(res => res.json())
.then(response => {
console.log()
res.value.push(response.data)
});
onInvalidate(() => controller.abort());
})
const change = (e) => {
search.value = e.target.value;
}
return {
search,
res,
change
}
}
})
app.mount("#app");
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 第17节 CompositionAPI3
- setup直接取代了
beforeCreate和created。beforeDestory和destroyed改为beforeUnmount和unmounted其他加一个on在setup中定义beforeCreate-> 使用 setup()created-> 使用 setup()- beforeMount -> onBeforeMount
- mounted -> onMounted
- beforeUpdate -> onBeforeUpdate
- updated -> onUpdated
- beforeUnmount -> onBeforeUnmount
- unmounted -> onUnmounted
- errorCaptured -> onErrorCaptured
- renderTracked -> onRenderTracked
- renderTriggered -> onRenderTriggered
- activated -> onActivated
- deactivated -> onDeactivated
- 并且可以同时定义多个同样的生命周期,都会按序执行
- 可以将生命周期函数抽出到一个hook里面,setup里面调用就行
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {
ref,
onBeforeMount,
onMounted,
onActivated,
onBeforeUpdate,
onUpdated,
onBeforeUnmount,
onUnmounted,
} from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const msg = ref('你好');
onBeforeMount(() => console.log('onBeforeMount'));
onMounted(() => console.log('onMounted'));
onActivated(() => console.log('onActivated'));
onBeforeUpdate(() => console.log('onBeforeUpdate'));
onUpdated(() => console.log('onUpdated'));
onBeforeUnmount(() => console.log('onBeforeUnmount'));
onUnmounted(() => console.log('onUnmounted'));
return {
msg,
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
- 父组件
注意:provide数据尽量是单向数据流,不让子组件进行修改。
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<button @click="change">父组件:哈</button>
<home></home>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Home from './components/Home.vue';
import { provide, ref, readonly } from 'vue';
export default {
components: {
Home,
},
setup() {
const msg = ref('哈哈哈');
provide('msg', readonly(msg));
const change = () => msg.value += '哈';
return {
msg,
change,
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
- 子组件
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<button @click="change">子组件:哈</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { inject } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let msg = inject('msg');
const change = () => msg.value += '呵'; // 无效,警告
return {
msg,
change,
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 将同一代码逻辑进行抽离,一般hook名字都是
use开头,如:useCounter
<template>
<div>
<div>计数:{{ counter }}</div>
<div>双倍计数:{{ double }}</div>
<button @click="decre">-1</button>
<button @click="incre">+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
function useCount() {
let counter = ref(0);
let double = computed(() => counter.value * 2);
const incre = () => counter.value++;
const decre = () => counter.value--;
return {
counter,
double,
incre,
decre,
}
}
export default {
setup() {
const {
counter,
double,
incre,
decre,
} = useCount();
return {
counter,
double,
incre,
decre,
}
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
- 动态改变title:useTitle
<template>
<div>
<div>哈哈哈</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, watchEffect } from 'vue';
function useTitle(text = '呵呵') {
let title = ref(text);
watchEffect(() => document.title = title.value);
return {
title
}
}
export default {
setup() {
let { title } = useTitle('啦啦啦');
setTimeout(() => title.value = "略略略", 1000);
}
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
定义计算鼠标方位的hook
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default function() {
let x = ref(0);
let y = ref(0);
const events = [
'mousemove',
'touchmove'
]
events.forEach(event => {
document.body.addEventListener(event, e => {
x.value = e.x || e.touches[0]?.clientX || 0;
y.value = e.y || e.touches[0]?.clientY || 0;
})
})
return { x, y }
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
使用hook
<template>
<div class="box">
<div class="position">
<div>x:{{ x }}</div>
<div>y:{{ y }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import usePosition from './utils/usePosition'
export default {
setup() {
let { x, y } = usePosition();
return {
x,
y
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.box {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
}
.position {
position: fixed;
bottom: 10px;
right: 10px
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
- 使用
script setup来直接编写setup函数,外部定义的props、components、emits可以用函数定义- defineProps
- defineEmits
父组件
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
<home :msg="readonlyMsg" @decre="decre"></home>
<button @click="change">改变</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import Home from './components/Home.vue';
import { defineComponent, ref, readonly } from 'vue';
let msg = ref('哈哈');
let readonlyMsg = readonly(msg);
const change = () => msg.value += '哈';
const decre = () => msg.value = msg.value.slice(0, -1)
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
子组件
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<button @click="decre">发射-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineProps, defineEmits } from 'vue';
let { msg } = defineProps([ 'msg' ]);
const emit = defineEmits(['decre']);
const decre = () => emit('decre')
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 编译流程:template -> render函数 -> vNode -> DOM节点
- h函数创建vNode
- 组件内可以边写render函数,render函数返回h函数的执行,得到vNode
- h函数:
- 入参1:tagName(String|Object|function)
- 入参2:attributes(Object|null)
- 入参3:content(String|Array|Object)
// 单个vue文件
<script>
import { h } from 'vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
render() {
return h(
'div',
null,
[
h('div', null, this.counter),
h('button', { onClick: () => this.counter++ }, '+1'),
h('button', { onClick: () => this.counter-- }, '-1'),
]
)
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 用setup替代
<script>
import { ref, h } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let counter = ref(1);
return () =>
h(
'div',
null,
[
h('div', null, counter.value),
h('button', { onClick: () => counter.value++ }, '+1'),
h('button', { onClick: () => counter.value-- }, '-1'),
]
)
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- vue3支持模板里面直接写jsx语法
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let counter = ref(0);
const incre = () => counter.value++;
const decre = () => counter.value--;
return () => (
<div>
<div>{ counter.value }</div>
<button onClick={ decre }>-1</button>
<button onClick={ incre }>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 使用插槽
<script>
import home from './components/Home.vue';
export default {
setup() {
return () => (
<div>
<div>父组件</div>
<home>{{ default: props => <div>呵呵</div>}}</home>
</div>
)
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
<script>
import { useSlots } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const slots = useSlots();
return () => (
<div>
<div>home组件</div>
{ slots.default ? slots.default() : <span>默认插槽</span> }
</div>
)
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 第18节 Vue高级
对DOM进行操作时使用自定义指令
- 局部通过组件内directives定义,setup内通过resolveDirective定义
- 全局通过app.directive定义
- 回调函数名称和VUE2有改变
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="msg" v-focus.aaa.bbb:hehe="'略略略'">
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const directives = {
focus: {
mounted(el, binding) {
console.log(binding);
el.focus();
},
// 在绑定元素的 attribute 或事件监听器被应用之前调用
created() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件挂载之前调用
beforeMount() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件挂载之后调用
// mounted() {},
// 在包含组件的 VNode 更新之前调用
beforeUpdate() {},
// 在包含组件的 VNode 及其子组件的 VNode 更新之后调用
updated() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件卸载之前调用
beforeUnmount() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件卸载之后调用
unmounted() {}
}
}
export default {
directives,
setup() {
let msg = ref('哈哈');
return {
msg
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
- 自定义
v-time指令,解析模板中的时间字母,替换成给定时间戳的时间。 - 也可以用相应的日期格式化库
dayjs
utils/fmtTime.js
const fmtFn = function(timeStamp, fmt) {
fmt = fmt ? fmt : 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss';
const fnMap = new Map([
['y', { fnName: 'getFullYear', reg: /\b[y]{2,4}\b/g }],
['M', { fnName: 'getMonth', reg: /\b[M]{2}\b/g }],
['d', { fnName: 'getDate', reg: /\b[d]{2}\b/g }],
['h', { fnName: 'getHours', reg: /\b[h]{2}\b/g }],
['m', { fnName: 'getMinutes', reg: /\b[m]{2}\b/g }],
['s', { fnName: 'getSeconds', reg: /\b[s]{2}\b/g }]
])
const date = new Date(+timeStamp);
if (Number.isNaN(date.getTime())) {
return Error('传入的非时间戳');
}
let isTrans = false;
fnMap.forEach(({fnName, reg}, key) => {
fmt = fmt.replace(reg, (match) => {
isTrans = true;
let len = match.length;
let time = key === 'M' ? date[fnName]() + 1 : date[fnName]();
let timeStr = time.toString();
return timeStr.slice(0 - len).padStart(len, '0');
})
})
if (!isTrans) {
console.error('格式化参数有误!');
}
return fmt;
}
const fmtTimeDir = {
mounted(el, binding) {
const timeStamp = +binding.value;
const fmt = el.innerText;
el.innerText = fmtFn(timeStamp, fmt);
}
}
export { fmtTimeDir }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
main.js,全局注册
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { fmtTimeDir } from './utils/formatTime'
const app = createApp(App);
app.directive('time', fmtTimeDir);
app.mount('#app')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
vue组件中使用
<template>
<div>
<div v-time="stamp">{{ msg }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let msg = ref('今年是yyyy,我很开心在MM月能够看到你,yyds,期望明年的MM月还能再看到你!');
const stamp = ref(+new Date());
return {
stamp,
msg
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
效果
- 定义挂载到app元素之外的模板里面
组件内部定义的
teleport标签,内容会被放到app挂载元素的外面,做一些特殊元素的展示。
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<teleport to="#hdy">
<div>哈哈哈,app外部</div>
</teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
let msg = ref('yyds');
return {
msg
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- 两种编写模式
- 对象:必须要有install方法,安装时执行
- 函数:安装插件时自动执行
- 可以完成的功能
- 全局添加properties、配置等
- 全局资源:过滤器、指令、filter等
- 全局mixin,合入一些组件选项
- 注入自己编写的一个库,提供一些自定义的API
export default {
install(app) {
app.config.globalProperties.$name = 'hdy';
}
}
2
3
4
5
app.use(myPlugin);
// options组件内使用,可以拿this
mounted() {
console.log(this.$name); // hdy
}
// setup组件内使用,不可以拿this
onMounted(() => {
const app = getCurrentInstance();
console.log(app.appContext.config.globalProperties.$name);
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 第19节 Vue原理
- 虚拟DOM的优势:
- 对真实DOM操作性能开销很大,diff算法也麻烦。
- 而用虚拟DOM,也就是JS对象进行操作性能会更高。
- 虚拟DOM有跨平台能力,将虚拟DOM转化成原生的控件。canvas/ssr/native(ios、android)
- Vue三大核心:
- compiler模块:模板语法编译系统
- runtime模块:renderer渲染系统
- reactivity模块:响应式系统
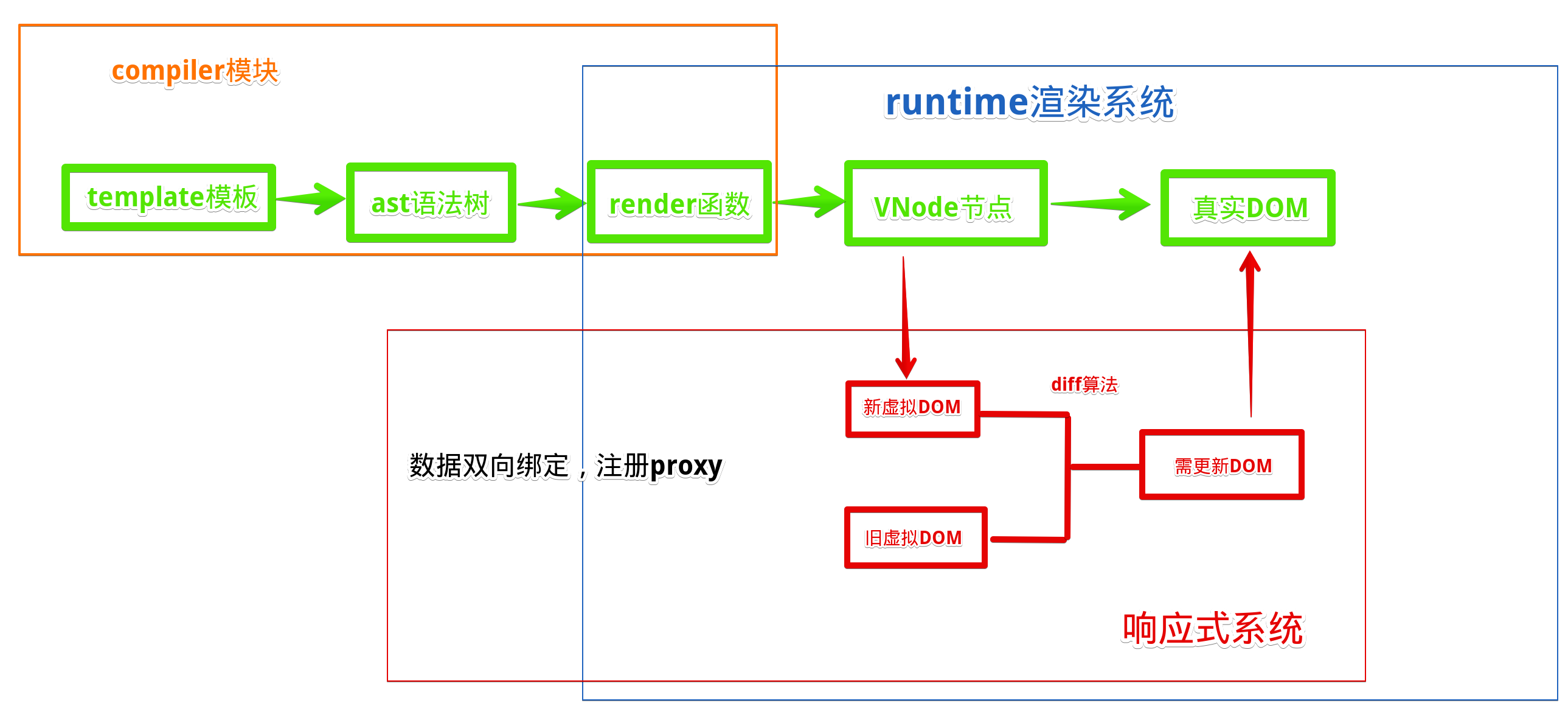
# 第20节 手写runtime模块
- 经过compiler模块,可以拿到ast语法树
- 然后就可以调用render函数,render函数调用h函数,h函数入参就是ast语法树生成的token和对应的语法
- h函数生成虚拟DOM,也就是一个JS对象,然后调用patch变成真实DOM。就会有两种情况
- 首次渲染,直接转换成真实DOM并挂载到对应的$el上
- 非首次渲染,会有过往的旧虚拟DOM,和旧的虚拟DOM进行diff算法,对比出更改的节点,只替换掉对应的节点。
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type='module' >
import h from './h.js';
import mount from './mount.js'
const VNode = h('div', { class: 'box' }, [
h('span', null, '你好,h函数'),
h('span', null, '你好,h函数'),
h('span', null, '你好,h函数'),
])
const app = document.querySelector('#app');
mount(app, VNode);
</script>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 作用:生成VNode
function h(tagName, props, children) {
return {
tagName,
props,
children
}
}
export default h;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 作用:VNode首次生成真实DOM挂载到对应节点上
function mount($el, VNode) {
// 后续diff算法patch上树需要用到真实DOM节点,先保存
const ele = VNode.$el = document.createElement(VNode.tagName);
if (VNode.props) {
Object.entries(VNode.props).forEach(([key, val]) => {
ele.setAttribute(key, val);
})
}
const { children } = VNode;
if (children) {
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
children.forEach(item => {
if (typeof item === 'object' && item != null && item.tagName != null) {
mount(ele, item);
} else {
ele.append(item);
}
})
} else {
ele.append(children);
}
}
$el.append(ele);
}
export default mount;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 数据更新,生成新的VNode,做diff算法,再替换指定的节点
- tagName不同,直接替换原节点
import mount from "./mount";
function patch(n1, n2) {
// diff tagName
if (n1.tagName !== n2.tagName) {
const n1Parent = n1.$el.parentElement;
n1Parent.removeChild(n1.$el);
mount(n1Parent, n2);
} else {
// diff props,新旧不同,新的为准;旧有新无,删除属性
const el = n2.$el = n1.$el;
const oldProps = n1.props || {};
const newProps = n2.props || {};
Object.entries(newProps).forEach(([key, val]) => {
if (oldProps[key] !== val) {
el.setAttribute(key, val);
}
})
Object.entries(oldProps).forEach(([key, val]) => {
if (!newProps[key]) {
el.removeAttribute(key);
}
})
// diff children
const oldChildren = n1.children || [];
const newChildren = n2.children || [];
if (typeof newChildren === 'string') {
// 子节点类型不同直接替换
if (oldChildren !== newChildren) {
el.innerHTML = '';
el.contentText = newChildren;
}
} else if (!Array.isArray(oldChildren)) {
// 旧节点不是数组,新节点是数组,直接挂新子节点
el.innerHTML = '';
newChildren.forEach(item => mount(el, item));
} else {
/**
* 新旧都是数组,diff算法。
* * 没有key,顺序遍历,逆序遍历,拿到不同,最大程度复用DOM就行。
* * 有key,用key去做新旧节点对比就行。
* >拿长度较短的进行遍历,防止指针溢出。
*/
const commonLength = Math.min(oldChildren.length, newChildren.length);
if (newChildren[0]?.props?.key == null) {
// 无key:顺序比较,性能较低
for (let i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {
patch(oldChildren[i], newChildren[i]);
}
if (newChildren.length > oldChildren.length) {
const appendList = newChildren.slice(commonLength);
appendList.forEach(item => mount(el, item));
} else if (newChildren.length < oldChildren.length) {
const delList = oldChildren.slice(commonLength);
delList.forEach(item => el.removeChild(item.$el));
}
} else {
console.log('有key的diff');
}
}
}
}
export default patch;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# 第21节 手写响应式模块
- 有一个Dep类,
subscribers副作用收集器,也就是依赖们,存的是函数,收集方式用Set,防止重复depend,收集副作用,也就是收集修改时对应的操作notify,数据发生改变的时候执行,通知subscribers里面所有的依赖的函数进行调用执行
- 全局一个
activeEffect变量,一个watchEffect收集effect targetMap用WeakMap为target所有的key收集deps,内部用Map进行绑定。- 一个
reactive函数,将原始对象转化成响应式对象返回出去。- 监听操作:
proxy或Object.defineProperty进行劫持,get收集依赖,set通知依赖
- 监听操作:
- Dep就是一个副作用收集器和触发器,watchEffect注册订阅者(副作用)的过程,就执行了一遍,也就是去取了依赖的变量,访问了getter
- 同时全局的activeEffect变量记录了当前在注册的订阅者是谁,所以在dep.depend()执行的时候能够拿到正确的订阅者。
class Dep {
subscribers = new Set();
depend() {
if (activeEffect) {
this.subscribers.add(activeEffect);
}
}
notify() {
this.subscribers.forEach(effect => effect());
}
}
let activeEffect = null;
function watchEffect(effect) {
activeEffect = effect;
effect();
activeEffect = null;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* watchEffect传入函数,默认会执行一遍。访问所有执行期间会访问的变量,让他收集依赖。
* 此时全局activeEffect是函数自身,收集器就能够正确的收集。
* 告诉他如果变量有改变通知我执行。
*/
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.name + '哈哈哈'));
2
3
4
5
6
- WeakMap存储所有的对象响应式对象,对应它们的deps
- 每个deps是一个Map,也就是响应式对象每个值对应的dep
// 根据对象,键,获取对应的Dep实例
const targetMap = new WeakMap();
function getDep(target, key) {
let depsMap = targetMap.get(target);
if (!depsMap) {
depsMap = new Map();
targetMap.set(target, depsMap);
}
let dep = depsMap.get(key);
if (!dep) {
dep = new Dep();
depsMap.set(key, dep);
}
return dep;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 注:defineProperty是一次性注册,也就是如果对象新增属性是没有响应式的。
所以Vue2新增属性要用
Vue.$set(obj, key, val)
// 将原生数据对象的所有数据做成响应式的
function reactive(raw) {
for (let key in raw) {
const dep = getDep(raw, key);
let val = raw[key];
Object.defineProperty(raw, key, {
get() {
dep.depend();
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal != val) {
val = newVal;
dep.notify();
}
}
})
}
return raw;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 生成响应式对象
let info = reactive({name: 'hdy', age: 18});
// 注册订阅者
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.name + '哈哈哈')); // hdy哈哈哈
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.name + '略略略')); // hdy略略略
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.name + '好多依赖啊')); // hdy好多依赖啊
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.age * 100)); // 1800
// 响应式测试
info.name = '张三会响应式了';
/**
* 张三会响应式了哈哈哈
* 张三会响应式了略略略
* 张三会响应式了好多依赖啊
*/
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 原理相同,只不过原生对象新增属性时,proxy也能做到响应式,而defineProperty不行。
- 因为proxy本质上是设置代理
- defineProperty本质上是给每个属性配置一遍dep
function reactive(raw) {
const proxy = new Proxy(raw, {
get(target,key) {
// 深度监听
if (typeof target[key] === 'object' && target[key] != null) {
target[key] = reactive(target[key]);
}
const dep = getDep(raw, key);
dep.depend();
return target[key];
},
set(target, key, val) {
if (target[key] !== val) {
target[key] = val;
const dep = getDep(raw, key);
dep.notify();
}
// MDN上说proxy的setter必须返回一个布尔值代表赋值成功或失败
return true;
}
});
return proxy;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
- proxy优势:新增属性也能响应式
let info = reactive({name: 'hdy', age: 18});
// 新增属性,以及依赖
info.book = '张三会响应式了';
watchEffect(() => console.log(info.book + '啦啦啦')); // 张三会响应式了啦啦啦
info.book = '你能监听?'; // 你能监听?啦啦啦
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 监听数组
let info = reactive([0, 1, 10, 20]);
// 新增
info.push(3);
watchEffect(() => console.log(info[4])); // 3
info[4] = '深度友谊iii~'; // 深度友谊iii~
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 第22节 setup使用VueX
- setup里面拿不到this,可以使用
useStore去拿store实例
<template>
<div>
{{ counter }}
<button @click="incre">app按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { computed } from 'vue';
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore();
let counter = computed(() => store.state.counter);
const incre = () => store.commit('addcounter');
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- store对象里面可以用mapState定义computed属性
import vuex, { mapState } from 'vuex';
const store = new vuex.Store({
state: {
counter: 0,
age: 18,
},
computed: mapState(['counter', 'age'])
});
export default store;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- setup里面可以用mapState拿到一堆计算属性的函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
setup() {
const storeStateFns = mapState(['counter', 'age']);
// storeStateFns: { counter: () => this.$store.state.counter }
}
2
3
4
5
- setup里面是拿不到this的,所以可以这么做:
import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex';
import { computed } from 'vue';
export default {
setup() {
const $store = useStore();
const storeState = {};
Object.entries(mapState(['counter', 'age'])).forEach(([key, fn]) => {
storeState[key] = computed(fn.bind({ $store })); // 重要:绑定this为store对象才能正确取值
})
return {
...storeState,
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 封装:src/hooks/useState
import { useStore, mapState } from 'vuex';
import { computed } from 'vue';
function useState(names) {
const $store = useStore();
if (typeof names === 'string') {
return computed(() => $store.state[names]);
} else if (typeof names === 'object' && names != null) {
const states = {};
Object.entries(mapState(names)).forEach(([key, fn]) => {
states[key] = computed(fn.bind({ $store }));
})
return states;
} else {
console.warn('useState接收数组或字符串');
return {}
}
}
export default useState;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
使用hook封装
import useState from './hooks/useState'
export default {
setup() {
const {counter, age} = useState(['counter', 'age']);
// 还可以使用改名
// let {sCounter, sAge} = useState({
// sCounter: state => state.counter,
// sAge: state => state.age,
// });
return {
counter,
age
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 定义
import vuex from 'vuex';
const store = new vuex.Store({
state: {
age: 18,
},
mutations: {
addAge(ctx) {
ctx.age++;
}
},
getters: {
myAge(state) {
return state.age + '岁'
}
}
});
export default store;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 普通使用
import { computed } from '@vue/runtime-core';
import { useStore } from 'vuex';
import useState from './hooks/useState'
export default {
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const age = computed(() => store.getters.myAge);
setTimeout(() => store.commit('addAge'), 2000)
return {
age
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
mapGetters将store定义的getters暴露出去。组件内用mapGetters去拿回来
import vuex, { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
const store = new vuex.Store({
state: {
age: 18,
},
mutations: {
addAge(ctx) {
ctx.age++;
}
},
getters: {
myAge(state) {
return state.age + '岁'
}
},
computed: mapGetters(['myAge'])
});
export default store;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
组件内mapGetters拿到的也是
{myAge: function() { return this.$store.getters.myAge}}的形式
所以需要绑定this并用computed做成响应式的
import { mapGetters, useStore } from 'vuex';
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const age = computed(() => mapGetters(['myAge']).myAge.bind({$store: store})());
setTimeout(() => store.commit('addAge'), 2000)
return {
age
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 封装hook:接收参数直接获取store的数据
import { computed } from 'vue';
import { mapGetters, useStore } from 'vuex';
function useGetters(keys) {
const $store = useStore();
if (typeof keys === 'object' && keys != null) {
const getters = {};
Object.entries(mapGetters(keys)).forEach(([key, fn]) => {
getters[key] = computed(fn.bind({ $store }));
})
return getters;
} else if (typeof keys === 'string') {
return $store.getters[keys].bind({ $store });
} else {
console.warn('useGetters接收参数错误');
return {};
}
}
export default useGetters;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
使用
import useGetters from './hooks/useGetters';
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const { age } = useGetters({
age: 'myAge'
});
// 或者
// const { myAge } = useGetters(['myAge']);
// const myAge = useGetters('myAge');
setTimeout(() => store.commit('addAge'), 2000)
return {
age
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 使用commit调用
const store = useStore();
store.commit('addCounter');
2
mapMutations可以直接将mutations拿到组件中直接使用。- 带参数写法:mutation需要入参的话,可以作commit的第二个参数,或者mapMutation拿到的第一个参数
import vuex, { mapGetters, mapMutations } from 'vuex';
const store = new vuex.Store({
state: {
age: 18,
},
mutations: {
increateN(ctx, n) {
ctx.age += n;
}
},
getters: {
myAge(state) {
return (str) => state.age + str;
}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(['myAge']),
...mapMutations(['increateN']),
}
});
export default store;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<script>
import useGetters from './hooks/useGetters';
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
setup() {
const myAge = useGetters('myAge');
const storeMmutations = mapMutations(['increateN']);
return {
myAge,
...storeMmutations
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
{{ myAge('岁') }}
<button @click="increateN(10)">+1</button>
</div>
</template>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- 第1节 介绍
- 第2节 class/style绑定
- 第3节 条件渲染/diff算法
- 第4节 watch/基础案例
- 第5节 v-model
- 第6节 组件化
- 第7节 webpack-loader
- 第8节 webpack-plugin
- 第9节 webpack-devServer
- 第10节 Vue-cli/vite
- 第11节 emit
- 第12节 组件通信
- 第13节 keep-alive/生命周期
- 第14节 动画
- 第15节 mixin/ConpositionAPI
- 第16节 ConpositionAPI2
- 第17节 CompositionAPI3
- 第18节 Vue高级
- 第19节 Vue原理
- 第20节 手写runtime模块
- 第21节 手写响应式模块
- 第22节 setup使用VueX
